Page 95 - DMGT104_FINANCIAL_ACCOUNTING
P. 95
Unit 6: Subsidiary Books
6.1 Meaning of Subsidiary Books Notes
In the past, traders use to keep record of the transaction in the journal. But it was later found not
convenient. If all the transaction is recorded in the journal then the journal book becomes more
thick and difficult to handle it. In big business houses, it becomes impossible to carry on the
work of recording business transaction. Therefore now a days large scale business firms like to
keep record of transaction in subsidiary books instead of journal. Subsidiary books are the book
of original entry and it is also called primary records because the first entry of transaction is
made in subsidiary books. Subsidiary Books refers to books meant for specific transactions of
similar nature. Subsidiary Books are also known as Special journals or day books. To overcome
shortcoming of the use of the journal only as a book of original entry, the journal is subdivided
into specific journals or subsidiary books. In practice, the journal is sub-divided in such a way
that a separate book is used for each category of transactions which are repetitive in nature and
are sufficiently large in number. In any large business the following subsidiary books are
generally used.
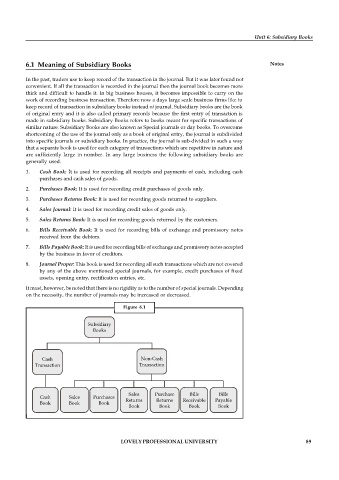
1. Cash Book: It is used for recording all receipts and payments of cash, including cash
purchases and cash sales of goods.
2. Purchases Book: It is used for recording credit purchases of goods only.
3. Purchases Returns Book: It is used for recording goods returned to suppliers.
4. Sales Journal: It is used for recording credit sales of goods only.
5. Sales Returns Book: It is used for recording goods returned by the customers.
6. Bills Receivable Book: It is used for recording bills of exchange and promissory notes
received from the debtors.
7. Bills Payable Book: It is used for recording bills of exchange and promissory notes accepted
by the business in favor of creditors.
8. Journal Proper: This book is used for recording all such transactions which are not covered
by any of the above mentioned special journals, for example, credit purchases of fixed
assets, opening entry, rectification entries, etc.
It must, however, be noted that there is no rigidity as to the number of special journals. Depending
on the necessity, the number of journals may be increased or decreased.
Figure 6.1
Subsidiary
Books
Cash Non-Cash
Transaction Transaction
Sales Purchase Bills Bills
Cash Sales Purchases
Returns Returns Receivable Payable
Book Book Book
Book Book Book Book
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 89