Page 105 - DMGT202_COST_AND_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 105
Cost and Management Accounting
Notes
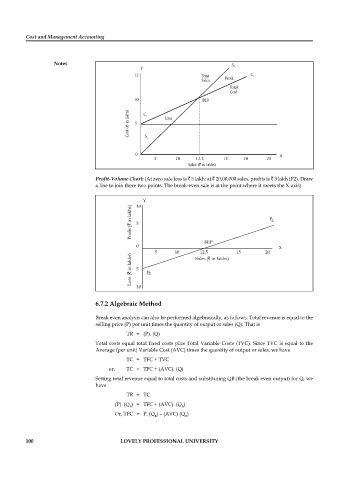
Y S 2
15 Total C 2
Sales Profit
Total
Cost
10 BEP
lakhs) C 1 Loss
in 5
(`
Cost S 1
0 X
5 10 12.5 15 20 25
Sales ( in lakhs)
`
Profi t-Volume Chart: (At zero sale loss is ` 5 lakh: at ` 20,00,000 sales, profi ts is ` 3 lakh (P2). Draw
a line to join there two points. The break-even sale is at the point where it meets the X-axis).
Y
10
in lakhs) P 2
Profit (` 5
BEP
0 X
5 10 12.5 15 20
in lakhs) 5 Sales ( in lakhs)
`
Loss (` P 1
10
6.7.2 Algebraic Method
Break even analysis can also be performed algebraically, as follows. Total revenue is equal to the
selling price (P) per unit times the quantity of output or sales (Q). That is
TR = (P). (Q)
Total costs equal total fixed costs plus Total Variable Costs (TVC). Since TVC is equal to the
Average (per unit) Variable Cost (AVC) times the quantity of output or sales, we have
TC = TFC + TVC
or, TC = TFC + (AVC). (Q)
Setting total revenue equal to total costs and substituting QB (the break even output) for Q, we
have
TR = TC
(P). (Q ) = TFC + (AVC). (Q )
B B
Or, TFC = P. (Q ) – (AVC) (Q )
B B
100 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY