Page 248 - DMGT501_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 248
Operations Management
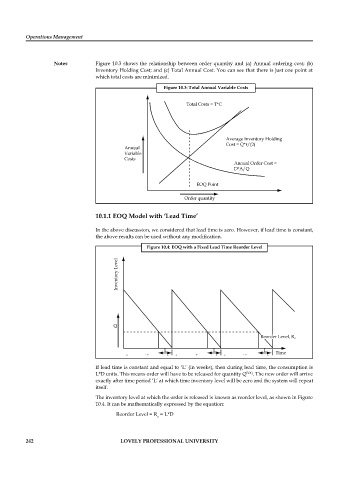
Notes Figure 10.3 shows the relationship between order quantity and (a) Annual ordering cost; (b)
Inventory Holding Cost; and (c) Total Annual Cost. You can see that there is just one point at
which total costs are minimized.
Figure 10.3: Total Annual Variable Costs
10.1.1 EOQ Model with ‘Lead Time’
In the above discussion, we considered that lead time is zero. However, if lead time is constant,
the above results can be used without any modification.
Figure 10.4: EOQ with a Fixed Lead Time Reorder Level
If lead time is constant and equal to ‘L’ (in weeks), then during lead time, the consumption is
L*D units. This means order will have to be released for quantity Q EOQ . The new order will arrive
exactly after time period ‘L’ at which time inventory level will be zero and the system will repeat
itself.
The inventory level at which the order is released is known as reorder level, as shown in Figure
10.4. It can be mathematically expressed by the equation:
Reorder Level = R = L*D
o
242 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY