Page 55 - DMGT501_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 55
Unit 2: Product and Service Design
Low Degree of Customer Contact Notes
Services, with a low degree of customer contact, involve the same stages as the design of
manufactured products. The service system product development process is comparable to
manufacturing shown in Figure 2.6.
However, services often do not require a physical component, such as prototype building, etc.,
and the process technology sometimes involves different issues and considerations because the
conversion process takes place before the client or customer.
High Degree of Customer Contact
Services with a high degree of customer contact are difficult to control as the customer can affect
the time of demand, the exact nature of the service, and the quality or the perceived quality of
the service. These types of services often require a high degree of personalization and speed of
delivery.
Services normally require a much higher levels of capacity relative to demand and also require
greater flexibility. There can be tremendous diversity of customer influence and hence greater
system variability.
2.12 Differences between Product Design and Service Design
The difference between manufactured goods and services serves as the basis for the difference in
their designs. Manufactured goods differ from services in three ways:
1. The first is that a good can be inventoried, thereby giving system designers additional
degrees of freedom.
2. The second difference relates to risk. More so than for services, the design of manufactured
products and their supporting delivery systems requires substantial up-front financial
commitments.
3. The third difference is that the product innovation process for goods are often supply
chain-wide dependent.
Example: For Intel to develop next-generation micro-processor chips, it requires co-
ordinate its efforts with software players, application developers and the makers of chip
manufacturing equipment.
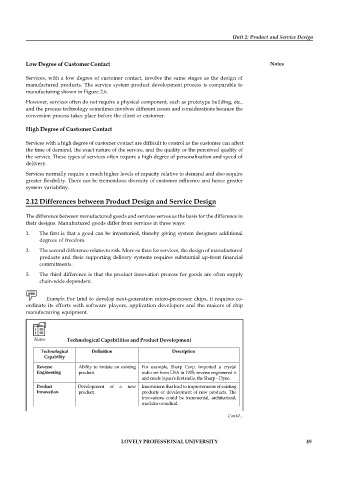
Notes Technological Capabilities and Product Development
Technological Definition Description
Capability
Reverse Ability to imitate an existing For example, Sharp Corp. imported a crystal
Engineering product. radio set from USA in 1925; reverse engineered it
and made Japan’s first radio, the Sharp – Dyne.
Product Development of a new Innovations that lead to improvements of existing
Innovation product. products or development of new products. The
innovations could be incremental, architectural,
modular or radical.
Process Improvements in process for Improvements in the manufacturing process,
Contd...
Innovation product manufacturing. integration of steps in the manufacturing process
leading to reductions in cycle time or reductions
in the number of process types, improving the
manufacturing process yields.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY method or
Application Utilisation of an existing idea Incorporation of a new idea, design 49
Innovation or concept for a new testing concept to improve, sometimes
application, or a new design, dramatically, existing products and processes. For
method or measurement example, the development of Nylon into material
technique. for use as tyre cords.
System Innovations involving Introduction of new systems through linking or
Innovations integration of sub-systems integration of a variety and sub-systems, and
and several innovations. involving product, process and application
innovations. For example, application of fuzzy
logic to improve continuous cold rolling mills in
steel manufacturing.
Core Competence Ability to leverage and Firm’s capability to innovate in all phases of
Leveraging enhance innovative activity innovation process, such as design, engineering,
Innovations from its areas of core testing and manufacturing, forms its core
competence: competence.
1. Expansion of innovation 1. An example is Hitachi’s ability to design and
in the different phases of produce 1MB DRAM in 1985, extended to 16
innovation. MB by 1990.
2. Extension of core 2. For example, Hitachi’s developments of the
competence horizontally world’s largest Ga-As single crystal and then
into a new field. using this technology in satellite
3. Fusing core competence broadcasting.
in different areas. 3. For example, thermostatic ceramic textiles are
a fusion of core competencies in textiles,
space and chemical technologies.