Page 10 - DMGT514_MANAGEMENT_CONTROL_SYSTEMS
P. 10
Unit 1: Introduction to Management Control System
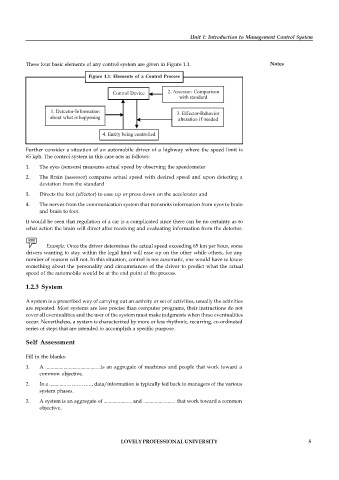
These four basic elements of any control system are given in Figure 1.1. Notes
Figure 1.1: Elements of a Control Process
Control Device 2. Assessor: Comparison
with standard
1. Detector-Information
3. Effector-Behavior
about what is happening alteration if needed
4. Entity being controlled
Further consider a situation of an automobile driver of a highway where the speed limit is
65 kph. The control system in this case acts as follows:
1. The eyes (sensors) measures actual speed by observing the speedometer
2. The Brain (assessor) compares actual speed with desired speed and upon detecting a
deviation from the standard
3. Directs the foot (effector) to ease up or press down on the accelerator and
4. The nerves from the communication system that transmits information from eyes to brain
and brain to foot.
It would be seen that regulation of a car is a complicated since there can be no certainty as to
what action the brain will direct after receiving and evaluating information from the detector.
Example: Once the driver determines the actual speed exceeding 65 km per hour, some
drivers wanting to stay within the legal limit will ease up on the other while others, for any
number of reasons will not. In this situation, control is not automatic, one would have to know
something about the personality and circumstances of the driver to predict what the actual
speed of the automobile would be at the end point of the process.
1.2.3 System
A system is a prescribed way of carrying out an activity or set of activities, usually the activities
are repeated. Most systems are less precise than computer programs, their instructions do not
cover all eventualities and the user of the system must make judgments when these eventualities
occur. Nevertheless, a system is characterized by more or less rhythmic, recurring, co-ordinated
series of steps that are intended to accomplish a specific purpose.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. A ...........................................is an aggregate of machines and people that work toward a
common objective.
2. In a ............……………., data/information is typically fed back to managers of the various
system phases.
3. A system is an aggregate of ...................... and ......................... that work toward a common
objective.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 5