Page 160 - DMGT514_MANAGEMENT_CONTROL_SYSTEMS
P. 160
Unit 7: Budgeting: Tool for Management Control
Advantages of Flexible Budgeting Notes
1. By giving allowance in accordance with the level of activity attained, the variances due to
volume, efficiency and spending can be analysed and appropriate action can be taken.
2. The management is able to assess the effect of their decisions. The deviation from budget
arising from a decision to vary the output can be studied.
3. It is useful for planning changes in the level of output.
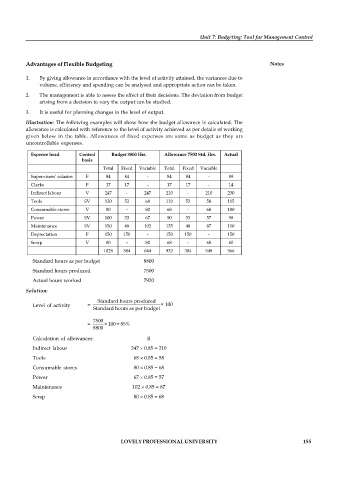
Illustration: The following examples will show how the budget allowance is calculated. The
allowance is calculated with reference to the level of activity achieved as per details of working
given below in the table. Allowances of fixed expenses are same as budget as they are
uncontrollable expenses.
Expense head Control Budget 8800 Hrs. Allowance 7500 Std. Hrs. Actual
basis
Total Fixed Variable Total Fixed Variable
Supervisors’ salaries F 84 84 - 84 84 - 89
Clerks F 17 17 – 17 17 - 14
Indirect labour V 247 - 247 210 - 210 230
Tools SV 120 52 68 110 52 58 115
Consumable stores V 80 – 80 68 - 68 100
Power SV 100 33 67 90 33 57 98
Maintenance SV 150 48 102 135 48 87 110
Depreciation F 150 150 - 150 150 - 150
Scrap V 80 – 80 68 - 68 60
1028 384 644 932 384 548 966
8800
Standard hours as per budget
Standard hours produced 7500
Actual hours worked 7920
Solution:
Standard hours produced
Level of activity = × 100
Standard hours as per budget
7500
= × 100 = 85%
8800
Calculation of allowances: R
Indirect labour 247 0.85 = 210
Tools 68 0.85 = 58
Consumable stores 80 0.85 = 68
Power 67 0.85 = 57
Maintenance 102 0.85 = 87
Scrap 80 0.85 = 68
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 155