Page 38 - DMGT514_MANAGEMENT_CONTROL_SYSTEMS
P. 38
Unit 3: Behavioural Considerations
2. Co-ordination becomes difficult between different functions for example: the marketing Notes
department may want to satisfy a customer’s need for a certain quantity of product even if
it involves over time work by the production which the latter is not willing to bear.
3. Functional structures are inadequate for a firm which has diversified products and markets.
Since the emphasis has to be different.
4. Functional organizations are inadequate for a firm which has diversified products and
markets since the emphasis has to be different
5. Functional organization tends to create ‘silos’ for each function thereby preventing cross-
functional organisation in areas such as new product development.
The management control process in a functional organisation works as follows:
1. The senior managers are responsible for developing the company’s overall strategy to
compete, in its chosen industry as well as its functional strategies in such areas as research
and development, manufacturing and marketing.
2. The plans for the organisation as a whole must be made at the very top (CEO’s level)
because these plans necessarily involves co-ordination of all the functions that contribute
to the final output. For example, plans for marketing dept, must take into account the
ability of the production departments to produce goods as per specification.
3. The strategic plan/long term planning involves only senior executives and a planning
staff. In a very small organisation the process may involve only CEO assisted by the
controller.
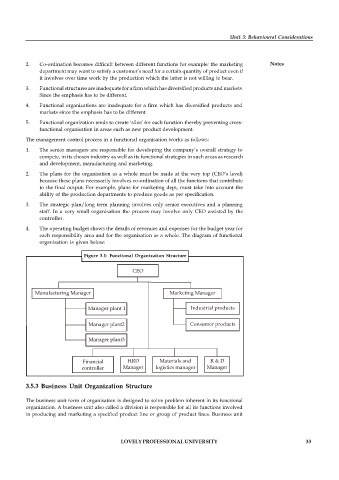
4. The operating budget shows the details of revenues and expenses for the budget year for
each responsibility area and for the organisation as a whole. The diagram of functional
organisation is given below:
Figure 3.1: Functional Organization Structure
CEO
Manufacturing Manager Marketing Manager
Manager plant 1 Industrial products
Manager plant2 Consumer products
Manager plant3
Financial HRD Materials and R & D
controller Manager logistics manager Manager
3.5.3 Business Unit Organization Structure
The business unit form of organisation is designed to solve problem inherent in its functional
organization. A business unit also called a division is responsible for all its functions involved
in producing and marketing a specified product line or group of product lines. Business unit
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 33