Page 39 - DMGT514_MANAGEMENT_CONTROL_SYSTEMS
P. 39
Management Control Systems
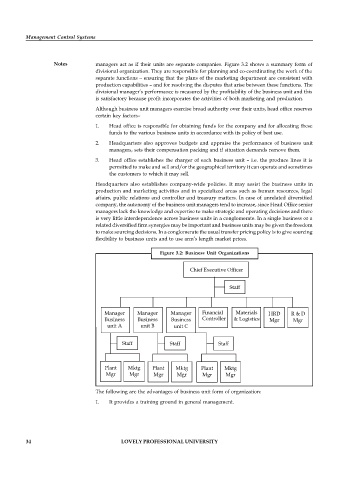
Notes managers act as if their units are separate companies. Figure 3.2 shows a summary form of
divisional organization. They are responsible for planning and co-coordinating the work of the
separate functions – ensuring that the plans of the marketing department are consistent with
production capabilities – and for resolving the disputes that arise between these functions. The
divisional manager’s performance is measured by the profitability of the business unit and this
is satisfactory because profit incorporates the activities of both marketing and production.
Although business unit managers exercise broad authority over their units, head office reserves
certain key factors–
1. Head office is responsible for obtaining funds for the company and for allocating these
funds to the various business units in accordance with its policy of best use.
2. Headquarters also approves budgets and appraise the performance of business unit
managers, sets their compensation packing and if situation demands remove them.
3. Head office establishes the charger of each business unit – i.e. the produce lines it is
permitted to make and sell and/or the geographical territory it can operate and sometimes
the customers to which it may sell.
Headquarters also establishes company-wide policies. It may assist the business units in
production and marketing activities and in specialized areas such as human resources, legal
affairs, public relations and controller and treasury matters. In case of unrelated diversified
company, the autonomy of the business unit managers tend to increase, since Head Office senior
managers lack the knowledge and expertise to make strategic and operating decisions and there
is very little interdependence across business units in a conglomerate. In a single business or a
related diversified firm synergies may be important and business units may be given the freedom
to make sourcing decisions. In a conglomerate the usual transfer pricing policy is to give sourcing
flexibility to business units and to use arm’s length market prices.
Figure 3.2: Business Unit Organizations
Chief Executive Officer
Staff
Manager Manager Manager Financial Materials HRD R & D
Business Business Business Controller & Logistics Mgr Mgr
unit A unit B unit C
Staff Staff Staff
Plant Mktg Plant Mktg Plant Mktg
Mgr Mgr Mgr Mgr Mgr Mgr
The following are the advantages of business unit form of organization:
1. It provides a training ground in general management.
34 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY