Page 179 - DMGT524_TOTAL_QUALITY_MANAGEMENT
P. 179
Total Quality Management
Notes 12.2.1 Risk Priority Numbers in FMEA
The Risk Priority Number (RPN) methodology is a technique for analyzing the risk associated
with potential problems identified during a Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA).
RPNs calculated at the level of the potential causes of failure (Severity × Occurrence × Detection).
The RPN method then requires the analysis team to use past experience and engineering judgment
to rate each potential problem according to three rating scales:
Severity, which rates the severity of the potential effect of the failure.
Occurrence, which rates the likelihood that the failure will occur.
Detection, which rates the likelihood that the problem will be detected before it reaches
the end-user/customer.
Rating scales usually range from 1 to 5 or from 1 to 10, with the higher number representing the
higher seriousness or risk. For example, on a ten point Occurrence scale, 10 indicate that the
failure is very likely to occur and is worse than 1, which indicates that the failure is very unlikely
to occur. The specific rating descriptions and criteria are defined by the organization or the
analysis team to fit the products or processes that are being analyzed.
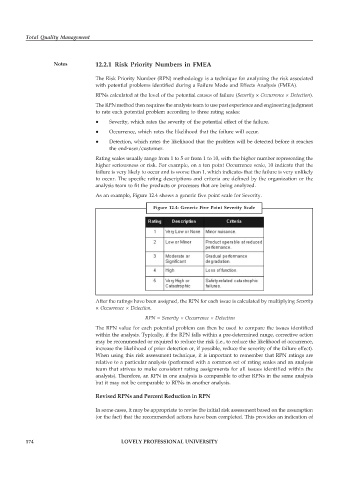
As an example, Figure 12.4 shows a generic five point scale for Severity.
Figure 12.4: Generic Five Point Severity Scale
After the ratings have been assigned, the RPN for each issue is calculated by multiplying Severity
× Occurrence × Detection.
RPN = Severity × Occurrence × Detection
The RPN value for each potential problem can then be used to compare the issues identified
within the analysis. Typically, if the RPN falls within a pre-determined range, corrective action
may be recommended or required to reduce the risk (i.e., to reduce the likelihood of occurrence,
increase the likelihood of prior detection or, if possible, reduce the severity of the failure effect).
When using this risk assessment technique, it is important to remember that RPN ratings are
relative to a particular analysis (performed with a common set of rating scales and an analysis
team that strives to make consistent rating assignments for all issues identified within the
analysis). Therefore, an RPN in one analysis is comparable to other RPNs in the same analysis
but it may not be comparable to RPNs in another analysis.
Revised RPNs and Percent Reduction in RPN
In some cases, it may be appropriate to revise the initial risk assessment based on the assumption
(or the fact) that the recommended actions have been completed. This provides an indication of
174 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY