Page 180 - DMGT524_TOTAL_QUALITY_MANAGEMENT
P. 180
Unit 12: Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
the effectiveness of corrective actions and can also be used to evaluate the value to the Notes
organization of performing the FMEA. To calculate revised RPNs, the analysis team assigns a
second set of Severity, Occurrence and Detection ratings for each issue (using the same rating
scales) and multiplies the revised ratings to calculate the revised RPNs. If both initial and
revised RPNs have been assigned, the percent reduction in RPN can also be calculated as follows:
RPN
RPN − r
i
% Reduction in RPN =
RPN i
For example, if the initial ratings for a potential problem are S = 7, O = 8 and D = 5 and the revised
ratings are S = 7, O = 6 and D = 4, then the percent reduction in RPN from initial to revised is (280-
168)/280, or 40%. This indicates that the organization was able to reduce the risk associated with
the issue by 40% through the performance of the FMEA and the implementation of corrective
actions.
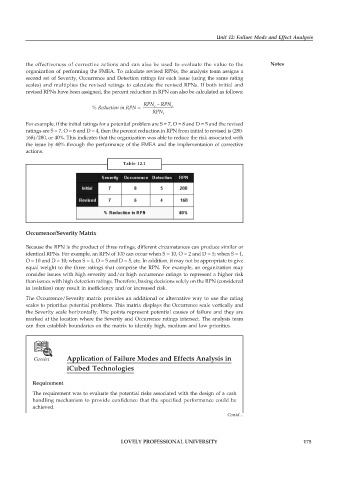
Table 12.1
Occurrence/Severity Matrix
Because the RPN is the product of three ratings, different circumstances can produce similar or
identical RPNs. For example, an RPN of 100 can occur when S = 10, O = 2 and D = 5; when S = 1,
O = 10 and D = 10; when S = 4, O = 5 and D = 5, etc. In addition, it may not be appropriate to give
equal weight to the three ratings that comprise the RPN. For example, an organization may
consider issues with high severity and/or high occurrence ratings to represent a higher risk
than issues with high detection ratings. Therefore, basing decisions solely on the RPN (considered
in isolation) may result in inefficiency and/or increased risk.
The Occurrence/Severity matrix provides an additional or alternative way to use the rating
scales to prioritize potential problems. This matrix displays the Occurrence scale vertically and
the Severity scale horizontally. The points represent potential causes of failure and they are
marked at the location where the Severity and Occurrence ratings intersect. The analysis team
can then establish boundaries on the matrix to identify high, medium and low priorities.
Caselet Application of Failure Modes and Effects Analysis in
iCubed Technologies
Requirement
The requirement was to evaluate the potential risks associated with the design of a cash
handling mechanism to provide confidence that the specified performance could be
achieved.
Contd...
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 175