Page 187 - DMGT549_INTERNATIONAL_FINANCIAL_MANAGEMENT
P. 187
International Financial Management
Notes The figures in brackets show the exchange rate used to translate the respective items in the
balance sheet.
Under the current rate method, the exchange loss is $300 because all accounts except net worth
are translated at the current exchange rate.
Problem 1:
Farm Products is the Canadian affiliate of a US manufacturing company. Its balance sheet, in
thousands of Canadian dollars, for January 1, 1991 is shown below. The January 1, 1991, exchange
rate was C$1.6/$.
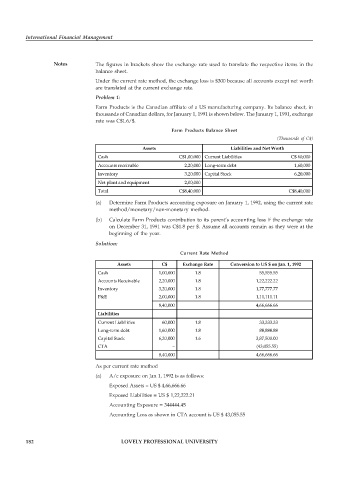
Farm Products Balance Sheet
(Thousands of C$)
Assets Liabilities and Net Worth
Cash C$1,00,000 Current Liabilities C$ 60,000
Accounts receivable 2,20,000 Long-term debt 1,60,000
Inventory 3,20,000 Capital Stock 6,20,000
Net plant and equipment 2,00,000
Total C$8,40,000 C$8,40,000
(a) Determine Farm Products accounting exposure on January 1, 1992, using the current rate
method/monetary/non-monetary method.
(b) Calculate Farm Products contribution to its parent’s accounting loss if the exchange rate
on December 31, 1991 was C$1.8 per $. Assume all accounts remain as they were at the
beginning of the year.
Solution:
Current Rate Method
Assets C$ Exchange Rate Conversion to US $ on Jan. 1, 1992
Cash 1,00,000 1.8 55,555.55
Accounts Receivable 2,20,000 1.8 1,22,222.22
Inventory 3,20,000 1.8 1,77,777.77
P&E 2,00,000 1.8 1,11,111.11
8,40,000 4,66,666.66
Liabilities
Current Liabilities 60,000 1.8 33,333.33
Long-term debt 1,60,000 1.8 88,888.88
Capital Stock 6,20,000 1.6 3,87,500.00
CTA – (43,055.55)
8,40,000 4,66,666.66
As per current rate method
(a) A/c exposure on Jan 1, 1992 is as follows:
Exposed Assets = US $ 4,66,666.66
Exposed Liabilities = US $ 1,22,222.21
Accounting Exposure = 344444.45
Accounting Loss as shown in CTA account is US $ 43,055.55
182 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY