Page 272 - DMGT206_PRODUCTION_AND_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 272
Unit 13: Production Planning and Control
Heuristic Steps 5-7: Repeat the above-explained process to get Table below. Note that we have Notes
used five workstations for the assignment of all the tasks. It could have been more.
Practical Example 1
If task ‘I’ required more time, we would have ended up with 6 workstations. This explains why
this is called the theoretical minimum workstations.
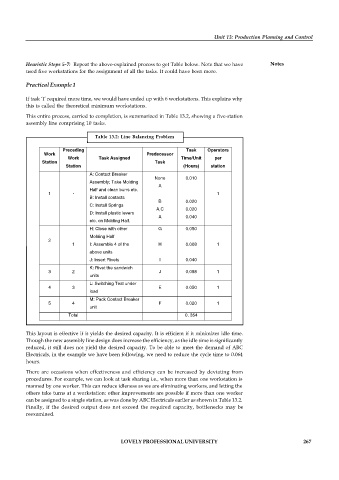
This entire process, carried to completion, is summarized in Table 13.2, showing a five-station
assembly line comprising 10 tasks.
Table 13.2: Line Balancing Problem
Preceding Task Operators
Work Predecessor
Work Task Assigned Time/Unit per
Station Task
Station (Hours) station
A: Contact Breaker
None 0.010
Assembly; Take Molding
A
Half and clean burrs etc.
1 - 1
B: Install contacts
B 0.020
C: Install Springs
A,C 0.020
D: Install plastic levers
A 0.040
etc. on Molding Half.
H: Close with other G 0.050
Molding Half
2
1 I: Assemble 4 of the H 0.008 1
above units
J: Insert Rivets I 0.040
K: Rivet the sandwich
3 2 J 0.098 1
units
L: Switching Test under
4 3 E 0.050 1
load
M: Pack Contact Breaker
5 4 F 0.020 1
unit
Total 0. 354
This layout is effective if it yields the desired capacity. It is efficient if it minimizes idle time.
Though the new assembly line design does increase the efficiency, as the idle time is significantly
reduced, it still does not yield the desired capacity. To be able to meet the demand of ABC
Electricals, in the example we have been following, we need to reduce the cycle time to 0.064
hours.
There are occasions when effectiveness and efficiency can be increased by deviating from
procedures. For example, we can look at task sharing i.e., when more than one workstation is
manned by one worker. This can reduce idleness as we are eliminating workers, and letting the
others take turns at a workstation: other improvements are possible if more than one worker
can be assigned to a single station, as was done by ABC Electricals earlier as shown in Table 13.2.
Finally, if the desired output does not exceed the required capacity, bottlenecks may be
reexamined.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 267