Page 128 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 128
Statistical Methods in Economics
Notes
P −
−
P −
( 90 P 50 ) ( 50 P 10 ) P + 90 P − 10 2P 50
Coefficient of S k = ( P P 50 ) 90 + ( − P − P 10 ) 50 = P − P 10
90
D + D − 2D
Coefficient of S k = 9 D − 1 D 1 5
9
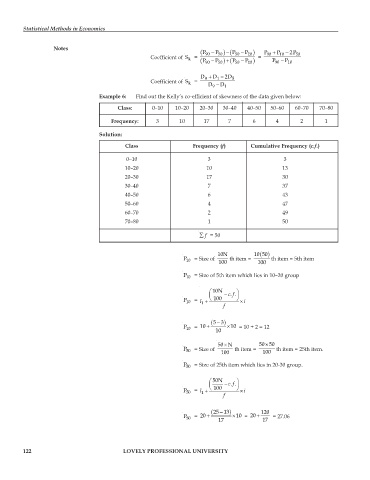
Example 6: Find out the Kelly’s co-efficient of skewness of the data given below:
Class: 0–10 10–20 20–30 30–40 40–50 50–60 60–70 70–80
Frequency: 3 10 17 7 6 4 2 1
Solution:
Class Frequency (f) Cumulative Frequency (c.f.)
0–10 3 3
10–20 10 13
20–30 17 30
30–40 7 37
40–50 6 43
50–60 4 47
60–70 2 49
70–80 1 50
∑ f = 50
( )
10N 10 50
P 10 = Size of 100 th item = 100 th item = 5th item
P 10 = Size of 5th item which lies in 10–20 group
⎛ ⎜ 10N − cf ⎞
.. ⎟
P 10 = l + ⎝ 100 ⎠ i ×
1
f
( − )53
P 10 = 10 + 10 × 10 = 10 + 2 = 12
×
50 N 50 50
×
P 50 = Size of 100 th item = 100 th item = 25th item.
P 50 = Size of 25th item which lies in 20-30 group.
⎛ 50N ⎞
⎜ − cf
.. ⎟
P 50 = l + ⎝ 100 ⎠ i ×
1
f
( − )25 13 120
P 50 = 20 + 17 × 10 = 20 + 17 = 27.06
122 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY