Page 154 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 154
Statistical Methods in Economics
Notes no linear relationship between the two variables. Correlations are rarely if ever 0, 1, or – 1. If you get
a certain outcome it could indicate whether correlations were negative or positive.
Mathematical Formula
The quantity r, called the linear correlation coefficient, measures the strength and the direction of a
linear relationship between two variables. The linear correlation coefficient is sometimes referred to
as the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient in honor of its developer Karl Pearson.
10.1 Scatter Diagram Method
The simplest device for determining relationship between two variables is a special type of dot chart
called scatter diagram. When this method is used the given data are plotted on a graph paper in the
form of dots, i.e., for each pair of X and Y values we put a dot and thus obtain as many points as the
number of observations. By looking to the scatter of the various points we can form an idea as to
whether the variables are related or not. The more the plotted points “scatter” over a chart, the less
relationship there is between the two variables. The more nearly the points come to falling on a line,
the higher the degree of relationship. If all the points lie on a straight line falling from the lower left-
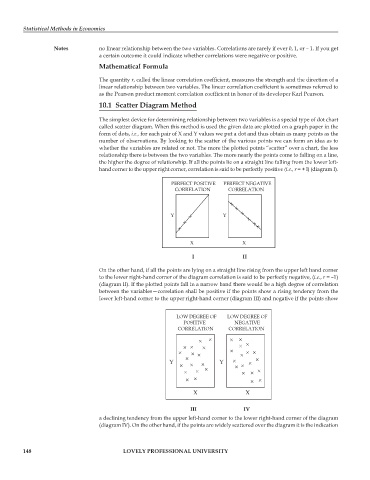
hand corner to the upper right corner, correlation is said to be perfectly positive (i.e., r = + l) (diagram I).
PERFECT POSITIVE PERFECT NEGATIVE
CORRELATION CORRELATION
Y Y
X X
I II
On the other hand, if all the points are lying on a straight line rising from the upper left hand corner
to the lower right-hand corner of the diagram correlation is said to be perfectly negative, (i.e., r = –1)
(diagram II). If the plotted points fall in a narrow band there would be a high degree of correlation
between the variables—correlation shall be positive if the points show a rising tendency from the
lower left-hand corner to the upper right-hand corner (diagram III) and negative if the points show
LOW DEGREE OF LOW DEGREE OF
POSITIVE NEGATIVE
CORRELATION CORRELATION
Y Y
X X
III IV
a declining tendency from the upper left-hand corner to the lower right-hand corner of the diagram
(diagram IV). On the other hand, if the points are widely scattered over the diagram it is the indication
148 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY