Page 288 - DCOM205_ACCOUNTING_FOR_COMPANIES_II
P. 288
Unit 12: Valuation of Shares
Solution Notes
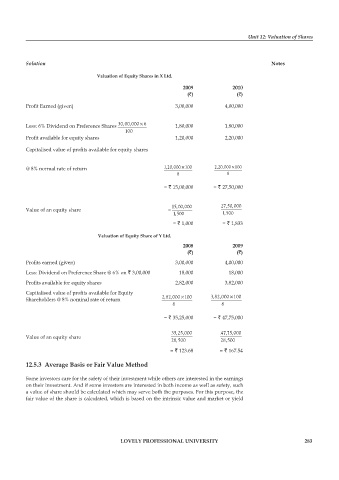
Valuation of Equity Shares in X Ltd.
2009 2010
(`) (`)
Profit Earned (given) 3,00,000 4,00,000
Rs.30,00,000 6
Less: 6% Dividend on Preference Shares × 1,80,000 1,80,000
100
Profit available for equity shares 1,20,000 2,20,000
Capitalised value of profits available for equity shares
×
×
@ 8% normal rate of return 1,20,000 100 2,20,000 100
8 8
= ` 15,00,000 = ` 27,50,000
Rs.15,00,000 Rs.27,50,000
Value of an equity share =
1,500 1,500
= ` 1,000 = ` 1,833
Valuation of Equity Share of Y Ltd.
2008 2009
(`) (`)
Profits earned (given) 3,00,000 4,00,000
Less: Dividend on Preference Share @ 6% on ` 3,00,000 18,000 18,000
Profits available for equity shares 2,82,000 3,82,000
Capitalised value of profits available for Equity
×
×
Shareholders @ 8% nominal rate of return Rs.2,82,000 100 Rs.3,82,000 100
8 8
= ` 35,25,000 = ` 47,75,000
Rs.35,25,000 Rs.47,75,000
Value of an equity share
28,500 28,500
= ` 123.68 = ` 167.54
12.5.3 Average Basis or Fair Value Method
Some investors care for the safety of their investment while others are interested in the earnings
on their investment. And if some investors are interested in both income as well as safety, such
a value of share should be calculated which may serve both the purposes. For this purpose, the
fair value of the share is calculated, which is based on the intrinsic value and market or yield
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 283