Page 125 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 125
Cost Accounting – II
Notes (x) Estimated amount of operating expenses on the basis of credit terms, agreement and
timing of disbursement,
(xi) Minimum cash balance desired depending upon business needs and market conditions,
and
(xii) Hire purchase and instalment sale agreement relating to instalment payments for purchase.
6.5.1 Role of Cash Budget
Efficient cash management through relevant and timely cash budgets may help:
(i) Provide funds for normal growth,
(ii) Secure optimum working capital needed for smooth and unhindered running of the
operation and planning for payments to shareholders,
(iii) Facilitate temporary investment of cash whenever, and to whatever extent, found in excess,
and
(iv) Ease strains of a cash shortage.
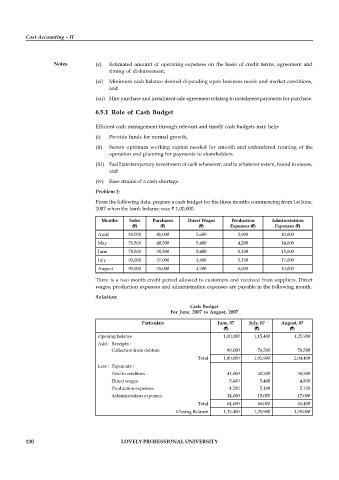
Problem 1:
From the following data, prepare a cash budget for the three months commencing from 1st June,
2007 when the bank balance was ` 1,00,000.
Months Sales Purchases Direct Wages Production Administration
(`) (`) (`) Expenses (`) Expenses (`)
April 80,000 41,000 5,600 3,900 10,000
May 76,500 40,500 5,400 4,200 14,000
June 78,500 38,500 5,400 5,100 15,000
July 90,000 37,000 4,800 5,100 17,000
August 95,000 35,000 4,700 6,000 13,000
There is a two month credit period allowed to customers and received from suppliers. Direct
wages, production expenses and administration expenses are payable in the following month.
Solution:
Cash Budget
For June, 2007 to August, 2007
Particulars June, 07 July, 07 August, 07
(`) (`) (`)
Opening balance 1,00,000 1,15,400 1,25,900
Add : Receipts :
Collection from debtors 80,000 76,500 78,500
Total 1,80,000 1,91,900 2,04,400
Less : Payments :
Paid to creditors 41,000 40,500 38,500
Direct wages 5,400 5,400 4,800
Production expenses 4,200 5,100 5,100
Administration expenses 14,000 15,000 17,000
Total 64,600 66,000 65,400
Closing Balance 1,15,400 1,25,900 1,39,000
120 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY