Page 126 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 126
Unit 6: Budgetary Control
Problem 2: Notes
Prepare a cash budget from the following data for three months from 1st April, 2007.
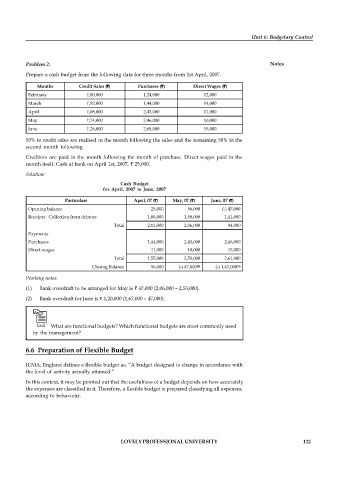
Months Credit Sales (`) Purchases (`) Direct Wages (`)
February 1,80,000 1,24,800 12,000
March 1,92,000 1,44,000 14,000
April 1,08,000 2,43,000 11,000
May 1,74,000 2,46,000 10,000
June 1,26,000 2,68,000 15,000
50% to credit sales are realised in the month following the sales and the remaining 50% in the
second month following.
Creditors are paid in the month following the month of purchase. Direct wages paid in the
month itself. Cash at bank on April 1st, 2007, ` 25,000.
Solution:
Cash Budget
for April, 2007 to June, 2007
Particulars April, 07 (`) May, 07 (`) June, 07 (`)
Opening balance 25,000 56,000 (-) 47,000
Receipts : Collection from debtors 1,86,000 1,50,000 1,41,000
Total 2,11,000 2,06,000 94,000
Payments :
Purchases 1,44,000 2,43,000 2,46,000
Direct wages 11,000 10,000 15,000
Total 1,55,000 2,53,000 2,61,000
Closing Balance 56,000 (-) 47,000 (-) 1,67,000
(1)
(2)
Working notes:
(1) Bank overdraft to be arranged for May is ` 47,000 (2,06,000 – 2,53,000).
(2) Bank overdraft for June is ` 1,20,000 (1,67,000 – 47,000).
Task What are functional budgets? Which functional budgets are most commonly used
by the management?
6.6 Preparation of Flexible Budget
ICMA, England defines a flexible budget as, “A budget designed to change in accordance with
the level of activity actually attained.”
In this context, it may be pointed out that the usefulness of a budget depends on how accurately
the expenses are classified in it. Therefore, a flexible budget is prepared classifying all expenses,
according to behaviour.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 121