Page 252 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 252
Unit 13: Activity-based Costing
From the above comparative analysis it is clear that, under Traditional Costing, Product X is Notes
charged with ` 105 per unit as manufacturing overheads while in case of Product Y, the share of
overhead cost is ` 140. Under Activity-based Costing the amount is ` 143.80 and ` 41.24 per unit.
Thus due to Activity-based Costing, the distortion in cost is avoided.
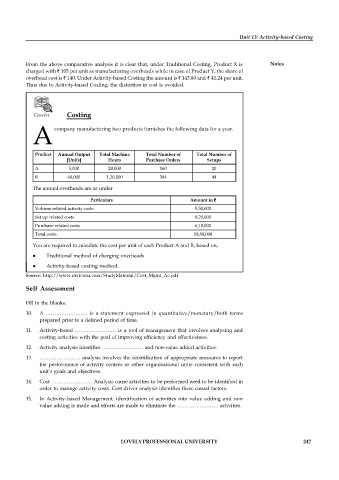
Caselet Costing
A company manufacturing two products furnishes the following data for a year.
Product Annual Output Total Machine Total Number of Total Number of
[Units] Hours Purchase Orders Setups
A 5,000 20,000 160 20
B 60,000 1,20,000 384 44
The annual overheads are as under
Particulars Amount in `
Volume related activity costs 5,50,000
Set up related costs 8,20,000
Purchase related costs 6,18,000
Total costs 19,88,000
You are required to calculate the cost per unit of each Product A and B, based on,
Traditional method of charging overheads
Activity-based costing method.
Source: http://www.myicwai.com/StudyMaterial/Cost_Mgmt_Ac.pdf
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
10. A …………………… is a statement expressed in quantitative/monetary/both terms
prepared prior to a defined period of time.
11. Activity-based …………………… is a tool of management that involves analysing and
costing activities with the goal of improving efficiency and effectiveness.
12. Activity analysis identifies …………………… and non-value added activities.
13. …………………… analysis involves the identification of appropriate measures to report
the performance of activity centres or other organisational units consistent with each
unit’s goals and objectives.
14. Cost …………………… Analysis cause activities to be performed need to be identified in
order to manage activity costs. Cost driver analysis identifies these casual factors.
15. In Activity-based Management, identification of activities into value adding and non
value adding is made and efforts are made to eliminate the …………………… activities.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 247