Page 253 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 253
Cost Accounting – II
Notes
Case Study Activity-based Costing
erris Corporation makes a single product – a fire resistant commercial filing cabinet –
that it sells to office furniture distributors. The company has a simple ABC system
Fthat it uses for internal decision making. The company has two overhead departments
whose costs are listed below:
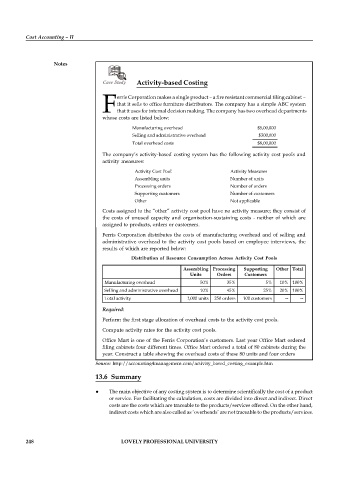
Manufacturing overhead $5,00,000
Selling and administrative overhead $300,000
Total overhead costs $8,00,000
The company’s activity-based costing system has the following activity cost pools and
activity measures:
Activity Cost Pool Activity Measures
Assembling units Number of units
Processing orders Number of orders
Supporting customers Number of customers
Other Not applicable
Costs assigned to the “other” activity cost pool have no activity measure; they consist of
the costs of unused capacity and organisation-sustaining costs - neither of which are
assigned to products, orders or customers.
Ferris Corporation distributes the costs of manufacturing overhead and of selling and
administrative overhead to the activity cost pools based on employee interviews, the
results of which are reported below:
Distribution of Resource Consumption Across Activity Cost Pools
Assembling Processing Supporting Other Total
Units Orders Customers
Manufacturing overhead 50% 35% 5% 10% 100%
Selling and administrative overhead 10% 45% 25% 20% 100%
Total activity 1,000 units 250 orders 100 customers -- --
Required:
Perform the first stage allocation of overhead costs to the activity cost pools.
Compute activity rates for the activity cost pools.
Office Mart is one of the Ferris Corporation’s customers. Last year Office Mart ordered
filing cabinets four different times. Office Mart ordered a total of 80 cabinets during the
year. Construct a table showing the overhead costs of these 80 units and four orders
Source: http://accounting4management.com/activity_based_costing_example.htm
13.6 Summary
The main objective of any costing system is to determine scientifically the cost of a product
or service. For facilitating the calculation, costs are divided into direct and indirect. Direct
costs are the costs which are traceable to the products/services offered. On the other hand,
indirect costs which are also called as ‘overheads’ are not traceable to the products/services.
248 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY