Page 79 - DCOM303_DMGT504_OPERATION_RESEARCH
P. 79
Operations Research
Notes 6x + 3x + 3x 150 (c)
1 2 3
where x , x , x 0
1 2 3
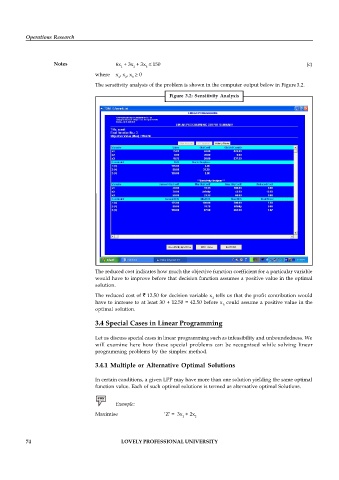
The sensitivity analysis of the problem is shown in the computer output below in Figure 3.2.
Figure 3.2: Sensitivity Analysis
The reduced cost indicates how much the objective function coefficient for a particular variable
would have to improve before that decision function assumes a positive value in the optimal
solution.
The reduced cost of ` 12.50 for decision variable x tells us that the profit contribution would
2
have to increase to at least 30 + 12.50 = 42.50 before x could assume a positive value in the
3
optimal solution.
3.4 Special Cases in Linear Programming
Let us discuss special cases in linear programming such as infeasibility and unboundedness. We
will examine here how these special problems can be recognised while solving linear
programming problems by the simplex method.
3.4.1 Multiple or Alternative Optimal Solutions
In certain conditions, a given LPP may have more than one solution yielding the same optimal
function value. Each of such optimal solutions is termed as alternative optimal Solutions.
Example:
Maximise ‘Z’ = 3x + 2x
1 2
74 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY