Page 32 - DCOM409_CONTEMPORARY_ACCOUNTING
P. 32
Unit 2: Price Level Accounting
Notes
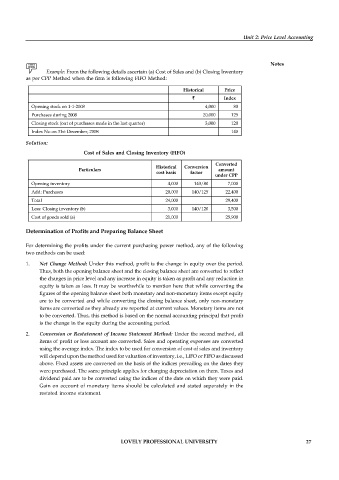
Example: From the following details ascertain (a) Cost of Sales and (b) Closing Inventory
as per CPP Method when the firm is following FIFO Method:
Historical Price
` Index
Opening stock on 1-1-2008 4,000 80
Purchases during 2008 20,000 125
Closing stock (out of purchases made in the last quarter) 3,000 120
Index No on 31st December, 2008 140
Solution:
Cost of Sales and Closing Inventory (FIFO)
Converted
Historical Conversion
Particulars amount
cost basis factor
under CPP
Opening inventory 4,000 140/80 7,000
Add: Purchases 20,000 140/125 22,400
Total 24,000 29,400
Less: Closing inventory (b) 3,000 140/120 3,500
Cost of goods sold (a) 21,000 25,900
Determination of Profits and Preparing Balance Sheet
For determining the profits under the current purchasing power method, any of the following
two methods can be used:
1. Net Change Method: Under this method, profit is the change in equity over the period.
Thus, both the opening balance sheet and the closing balance sheet are converted to reflect
the changes in price level and any increase in equity is taken as profit and any reduction in
equity is taken as loss. It may be worthwhile to mention here that while converting the
figures of the opening balance sheet both monetary and non-monetary items except equity
are to be converted and while converting the closing balance sheet, only non-monetary
items are converted as they already are reported at current values. Monetary items are not
to be converted. Thus, this method is based on the normal accounting principal that profit
is the change in the equity during the accounting period.
2. Conversion or Restatement of Income Statement Method: Under the second method, all
items of profit or loss account are converted. Sales and operating expenses are converted
using the average index. The index to be used for conversion of cost of sales and inventory
will depend upon the method used for valuation of inventory, i.e., LIFO or FIFO as discussed
above. Fixed assets are converted on the basis of the indices prevailing on the dates they
were purchased. The same principle applies for charging depreciation on them. Taxes and
dividend paid are to be converted using the indices of the date on which they were paid.
Gain on account of monetary items should be calculated and stated separately in the
restated income statement.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 27