Page 9 - DCOM505_WORKING_CAPITAL_MANAGEMENT
P. 9
Working Capital Management
Notes
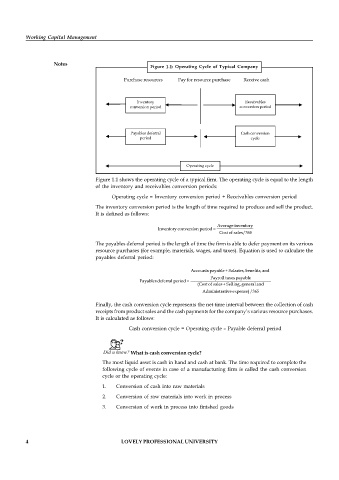
Figure 1.1: Operating Cycle of Typical Company
Purchase resources Pay for resource purchase Receive cash
Inventory Receivables
conversion period conversion period
Payables deferral Cash conversion
period cycle
Operating cycle
Figure 1.1 shows the operating cycle of a typical firm. The operating cycle is equal to the length
of the inventory and receivables conversion periods:
Operating cycle = Inventory conversion period + Receivables conversion period
The inventory conversion period is the length of time required to produce and sell the product.
It is defined as follows:
Average inventory
Inventory conversion period =
Cost of sales/365
The payables deferral period is the length of time the firm is able to defer payment on its various
resource purchases (for example, materials, wages, and taxes). Equation is used to calculate the
payables deferral period:
Accounts payable + Salaries, benefits, and
Payroll taxes payable
Payables deferral period =
(Cost of sales + Selling, general and
Administrative expense) /365
Finally, the cash conversion cycle represents the net time interval between the collection of cash
receipts from product sales and the cash payments for the company’s various resource purchases.
It is calculated as follows:
Cash conversion cycle = Operating cycle – Payable deferral period
Did u know? What is cash conversion cycle?
The most liquid asset is cash in hand and cash at bank. The time required to complete the
following cycle of events in case of a manufacturing firm is called the cash conversion
cycle or the operating cycle:
1. Conversion of cash into raw materials
2. Conversion of raw materials into work in process
3. Conversion of work in process into finished goods
4 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY