Page 167 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 167
Digital Circuits and Logic Design
Notes
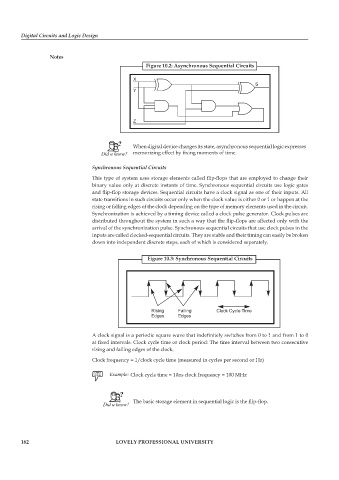
Figure 10.2: Asynchronous Sequential Circuits
X
S
Y
Z
When digital device changes its state, asynchronous sequential logic expresses
memorizing effect by fixing moments of time.
Synchronous Sequential Circuits
This type of system uses storage elements called flip-flops that are employed to change their
binary value only at discrete instants of time. Synchronous sequential circuits use logic gates
and flip-flop storage devices. Sequential circuits have a clock signal as one of their inputs. All
state transitions in such circuits occur only when the clock value is either 0 or 1 or happen at the
rising or falling edges of the clock depending on the type of memory elements used in the circuit.
Synchronization is achieved by a timing device called a clock pulse generator. Clock pulses are
distributed throughout the system in such a way that the flip-flops are affected only with the
arrival of the synchronization pulse. Synchronous sequential circuits that use clock pulses in the
inputs are called clocked-sequential circuits. They are stable and their timing can easily be broken
down into independent discrete steps, each of which is considered separately.
Figure 10.3: Synchronous Sequential Circuits
A clock signal is a periodic square wave that indefinitely switches from 0 to 1 and from 1 to 0
at fixed intervals. Clock cycle time or clock period: The time interval between two consecutive
rising and falling edges of the clock.
Clock frequency = 1/clock cycle time (measured in cycles per second or Hz)
Clock cycle time = 10ns clock frequency = 100 MHz
The basic storage element in sequential logic is the flip-flop.
162 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY