Page 176 - DCAP601_SIMULATION_AND_MODELING
P. 176
Simulation and Modelling
Notes How does it work?
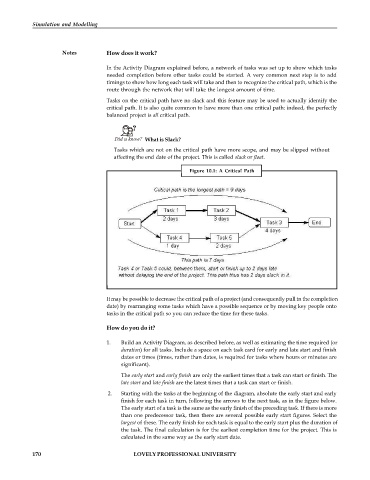
In the Activity Diagram explained before, a network of tasks was set up to show which tasks
needed completion before other tasks could be started. A very common next step is to add
timings to show how long each task will take and then to recognize the critical path, which is the
route through the network that will take the longest amount of time.
Tasks on the critical path have no slack and this feature may be used to actually identify the
critical path. It is also quite common to have more than one critical path: indeed, the perfectly
balanced project is all critical path.
Did u know? What is Slack?
Tasks which are not on the critical path have more scope, and may be slipped without
affecting the end date of the project. This is called slack or float.
Figure 10.1: A Critical Path
It may be possible to decrease the critical path of a project (and consequently pull in the completion
date) by rearranging some tasks which have a possible sequence or by moving key people onto
tasks in the critical path so you can reduce the time for these tasks.
How do you do it?
1. Build an Activity Diagram, as described before, as well as estimating the time required (or
duration) for all tasks. Include a space on each task card for early and late start and finish
dates or times (times, rather than dates, is required for tasks where hours or minutes are
significant).
The early start and early finish are only the earliest times that a task can start or finish. The
late start and late finish are the latest times that a task can start or finish.
2. Starting with the tasks at the beginning of the diagram, absolute the early start and early
finish for each task in turn, following the arrows to the next task, as in the figure below.
The early start of a task is the same as the early finish of the preceding task. If there is more
than one predecessor task, then there are several possible early start figures. Select the
largest of these. The early finish for each task is equal to the early start plus the duration of
the task. The final calculation is for the earliest completion time for the project. This is
calculated in the same way as the early start date.
170 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY