Page 212 - DMGT104_FINANCIAL_ACCOUNTING
P. 212
2007
2006
Decrease
Increase
(Credit)
(Debit)
( )
( )
( )
( )
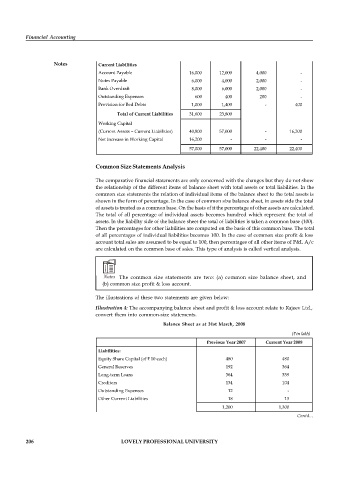
Current Assets
Cash in Hand
-
4,000
10,000
14,000
Book Debts
22,000
2,000
-
24,000
Cash at Bank Particulars 31 st March 31 st March Charges in Working Capital
14,000
18,000
4,000
-
Inventory 8,000 6,000 - 2,000
B/R 4,000 3,000 - 1,000
Prepaid Expenses 400 600 200 -
Financial Accounting Short-term Investments 10,000 16,000 6,000 -
Accured Interest 2,000 1,200 - 800
Total Current Assets 72,400 80,800
Notes Current Liabilities
Account Payable 16,000 12,000 4,000 -
Notes Payable 6,000 4,000 2,000 -
Bank Overdraft 8,000 6,000 2,000 -
Outstanding Expenses 600 400 200 -
Provision for Bed Debts 1,000 1,400 - 400
Total of Current Liabilities 31,600 23,800
Working Capital
(Current Assets – Current Liabilities) 40,800 57,000 - 16,200
Net Increase in Working Capital 16,200 - - -
57,000 57,000 22,400 22,400
Common Size Statements Analysis
The comparative financial statements are only concerned with the changes but they do not show
the relationship of the different items of balance sheet with total assets or total liabilities. In the
common size statements the relation of individual items of the balance sheet to the total assets is
shown in the form of percentage. In the case of common size balance sheet, in assets side the total
of assets is treated as a common base. On the basis of it the percentage of other assets are calculated.
The total of all percentage of individual assets becomes hundred which represent the total of
assets. In the liability side of the balance sheet the total of liabilities is taken a common base (100).
Then the percentages for other liabilities are computed on the basis of this common base. The total
of all percentages of individual liabilities becomes 100. In the case of common size profit & loss
account total sales are assumed to be equal to 100, then percentages of all other items of P&L A/c
are calculated on the common base of sales. This type of analysis is called vertical analysis.
Notes The common size statements are two: (a) common size balance sheet, and
(b) common size profit & loss account.
The illustrations of these two statements are given below:
Illustration 4: The accompanying balance sheet and profit & loss account relate to Rajeev Ltd.,
convert them into common-size statements.
Balance Sheet as at 31st March, 2008
( in lakh)
Previous Year 2007 Current Year 2008
Liabilities:
Equity Share Capital (of 10 each) 480 480
General Reserves 192 364
Long-term Loans 364 339
Creditors 134 104
Outstanding Expenses 12 -
Other Current Liabilities 18 13
1,200 1,300
Assets: Contd...
Plant 804 780
Cash 108 156
Debtors 120 130
206 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY
Inventories 168 234
1,200 1,300