Page 214 - DMGT104_FINANCIAL_ACCOUNTING
P. 214
(Percentage)
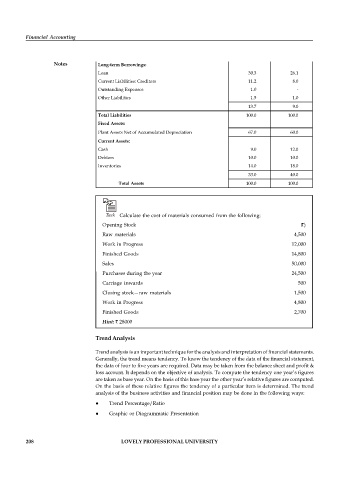
Particulars Previous year Current year
Owner's Equity
Financial Accounting Equity Share Capital 40.0 36.9
General Reserves 16.0 28.0
56.0 64.9
Notes Long-term Borrowings:
Loan 30.3 26.1
Current Liabilities: Creditors 11.2 8.0
Outstanding Expenses 1.0 -
Other Liabilities 1.5 1.0
13.7 9.0
Total Liabilities 100.0 100.0
Fixed Assets:
Plant Assets Net of Accumulated Depreciation 67.0 60.0
Current Assets:
Cash 9.0 12.0
Debtors 10.0 10.0
Inventories 14.0 18.0
33.0 40.0
Total Assets 100.0 100.0
Task Calculate the cost of materials consumed from the following:
Opening Stock ( )
Raw materials 4,500
Work in Progress 12,000
Finished Goods 14,800
Sales 50,000
Purchases during the year 24,500
Carriage inwards 500
Closing stock—raw materials 1,500
Work in Progress 4,800
Finished Goods 2,700
Hint: 28000
Trend Analysis
Trend analysis is an important technique for the analysis and interpretation of financial statements.
Generally, the trend means tendency. To know the tendency of the data of the financial statement,
the data of four to five years are required. Data may be taken from the balance sheet and profit &
loss account. It depends on the objective of analysis. To compute the tendency one year’s figures
are taken as base year. On the basis of this base year the other year’s relative figures are computed.
On the basis of these relative figures the tendency of a particular item is determined. The trend
analysis of the business activities and financial position may be done in the following ways:
Trend Percentage/Ratio
Graphic or Diagrammatic Presentation
208 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY