Page 71 - DMGT514_MANAGEMENT_CONTROL_SYSTEMS
P. 71
Management Control Systems
Notes Use of Profit Centre as a Measurement of Performance
The profit centre as a measurement of performance can be used for the following purposes:
1. Evaluation and ranking of profit centres: This can be done in relation to various types of
profit goals. As discussed in earlier paragraphs, the various profit goals with reference to
profit centre performance are: controllable contribution margin, controllable segment
margin, segment profit contribution, contribution margin ratio, segment profit
contribution rate and so on. In evaluating profit centers, we have to see whether individual
segments have achieved their objectives and ranking can be given based on comparative
performance of different segments.
2. Decisions to modify operations of profit centres: Profit centre performance assessment,
guides decisions to modify operations of the profit centres. Modification in this context
means expansion, contraction, addition or closure of the profit centre. The decision criterion
in such cases would be the incremental effect on the overall profits of the company. In the
short-run, assuming all attributable segment costs as constant, expansion or contraction in
a profit centre operation will affect the controllable contribution margin (since in short-
run, controllable fixed cost of the segment does not change).
In the long-run, changes in controllable fixed costs or attributable segment costs are to be
considered. Similarly, how the decision will affect the common firm wide costs or the
profit performance of other segments, are also to be considered.
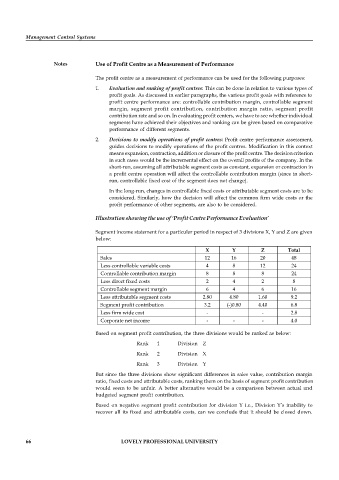
Illustration showing the use of ‘Profit Centre Performance Evaluation’
Segment income statement for a particular period in respect of 3 divisions X, Y and Z are given
below:
X Y Z Total
Sales 12 16 20 48
Less controllable variable costs 4 8 12 24
Controllable contribution margin 8 8 8 24
Less direct fixed costs 2 4 2 8
Controllable segment margin 6 4 6 16
Less attributable segment costs 2.80 4.80 1.60 9.2
Segment profit contribution 3.2 (-)0.80 4.40 6.8
Less firm wide cost - - 2.8
Corporate net income - - - 4.0
Based on segment profit contribution, the three divisions would be ranked as below:
Rank 1 Division Z
Rank 2 Division X
Rank 3 Division Y
But since the three divisions show significant differences in sales value, contribution margin
ratio, fixed costs and attributable costs, ranking them on the basis of segment profit contribution
would seem to be unfair. A better alternative would be a comparison between actual and
budgeted segment profit contribution.
Based on negative segment profit contribution for division Y i.e., Division Y’s inability to
recover all its fixed and attributable costs, can we conclude that it should be closed down.
66 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY