Page 97 - DMGT514_MANAGEMENT_CONTROL_SYSTEMS
P. 97
Management Control Systems
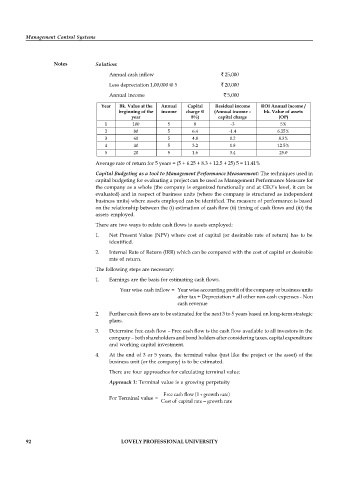
Notes Solution:
Annual cash inflow ` 25,000
Less depreciation 1,00,000 @ 5 ` 20,000
Annual income ` 5,000
Year Bk. Value at the Annual Capital Residual income ROI Annual income /
beginning of the income charge @ (Annual income – bk. Value of assets
year 8%) capital charge (OP)
1 100 5 8 -3 5%
2 80 5 6.4 -1.4 6.25%
3 60 5 4.8 0.2 8.3%
4 40 5 3.2 1.8 12.5%
5 20 5 1.6 3.4 25.0
Average rate of return for 5 years = (5 + 6.25 + 8.3 + 12.5 + 25) 5 = 11.41%
Capital Budgeting as a tool to Management Performance Measurement: The techniques used in
capital budgeting for evaluating a project can be used as Management Performance Measure for
the company as a whole (the company is organized functionally and at CEO’s level, it can be
evaluated) and in respect of business units (where the company is structured as independent
business units) where assets employed can be identified. The measure of performance is based
on the relationship between the (i) estimation of cash flow (ii) timing of cash flows and (iii) the
assets employed.
There are two ways to relate cash flows to assets employed:
1. Net Present Value (NPV) where cost of capital (or desirable rate of return) has to be
identified.
2. Internal Rate of Return (IRR) which can be compared with the cost of capital or desirable
rate of return.
The following steps are necessary:
1. Earnings are the basis for estimating cash flows.
Year wise cash inflow = Year wise accounting profit of the company or business units
after tax + Depreciation + all other non-cash expenses - Non
cash revenue
2. Further cash flows are to be estimated for the next 3 to 5 years based on long-term strategic
plans.
3. Determine free cash flow – Free cash flow is the cash flow available to all investors in the
company – both shareholders and bond holders after considering taxes, capital expenditure
and working capital investment.
4. At the end of 3 or 5 years, the terminal value (just like the project or the asset) of the
business unit (or the company) is to be estimated.
There are four approaches for calculating terminal value:
Approach 1: Terminal value is a growing perpetuity
For Terminal value =
92 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY