Page 121 - DMGT524_TOTAL_QUALITY_MANAGEMENT
P. 121
Total Quality Management
Notes Six Sigma uses a variety of statistics to determine the best practices for any given process.
Statisticians and Six Sigma consultants study the existing processes and determine the methods
that produce the best overall results. Combinations of these methods will be tested and upon
determining that a given combination can improve the process, it will be implemented.
Did u know? Six Sigma stands for “Six Standard deviations from the arithmetic mean”.
Six Sigma statistically ensures that 99.9997% of all products produced in a process are of acceptable
quality. Six Sigma allows only 3.4 defects per million opportunities. If a given process fails to
meet this criterion, it is reanalyzed, altered and tested to find out if there are any improvements.
If no improvement is found, the process is reanalyzed, altered and tested again. This cycle is
repeated until you see an improvement.
Once an improvement is found, it is documented and the knowledge is spread across other units
in the company so they can implement this new process and reduce their defects per million
opportunities.
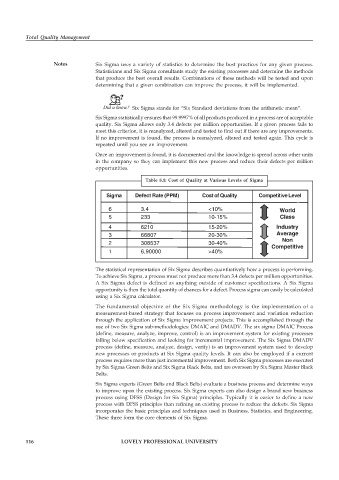
Table 8.1: Cost of Quality at Various Levels of Sigma
Sigma Defect rate (PPM) Cost of quality Competitive level
Cost of Quality
Competitive Level
Sigma
Defect Rate (PPM)
6 3.4 <10% World
5 233 10-15% Class
4 6210 15-20% Industry
3 66807 20-30% Average
Non
2 308537 30-40%
Competitive
1 6,90000 >40%
The statistical representation of Six Sigma describes quantitatively how a process is performing.
To achieve Six Sigma, a process must not produce more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
A Six Sigma defect is defined as anything outside of customer specifications. A Six Sigma
opportunity is then the total quantity of chances for a defect. Process sigma can easily be calculated
using a Six Sigma calculator.
The fundamental objective of the Six Sigma methodology is the implementation of a
measurement-based strategy that focuses on process improvement and variation reduction
through the application of Six Sigma improvement projects. This is accomplished through the
use of two Six Sigma sub-methodologies: DMAIC and DMADV. The six sigma DMAIC Process
(define, measure, analyze, improve, control) is an improvement system for existing processes
falling below specification and looking for incremental improvement. The Six Sigma DMADV
process (define, measure, analyze, design, verify) is an improvement system used to develop
new processes or products at Six Sigma quality levels. It can also be employed if a current
process requires more than just incremental improvement. Both Six Sigma processes are executed
by Six Sigma Green Belts and Six Sigma Black Belts, and are overseen by Six Sigma Master Black
Belts.
Six Sigma experts (Green Belts and Black Belts) evaluate a business process and determine ways
to improve upon the existing process. Six Sigma experts can also design a brand new business
process using DFSS (Design for Six Sigma) principles. Typically it is easier to define a new
process with DFSS principles than refining an existing process to reduce the defects. Six Sigma
incorporates the basic principles and techniques used in Business, Statistics, and Engineering.
These three form the core elements of Six Sigma.
116 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY