Page 239 - DMGT524_TOTAL_QUALITY_MANAGEMENT
P. 239
Total Quality Management
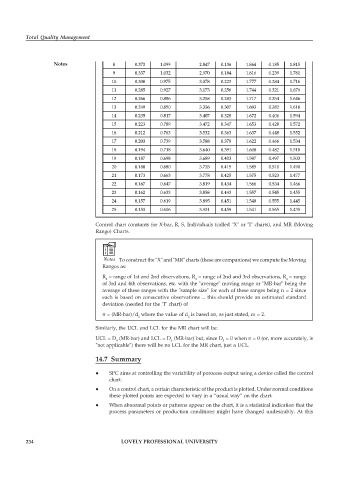
Notes 8 0.373 1.099 2.847 0.136 1.864 0.185 1.815
9 0.337 1.032 2.970 0.184 1.816 0.239 1.761
10 0.308 0.975 3.078 0.223 1.777 0.284 1.716
11 0.285 0.927 3.173 0.256 1.744 0.321 1.679
12 0.266 0.886 3.258 0.283 1.717 0.354 1.646
13 0.249 0.850 3.336 0.307 1.693 0.382 1.618
14 0.235 0.817 3.407 0.328 1.672 0.406 1.594
15 0.223 0.789 3.472 0.347 1.653 0.428 1.572
16 0.212 0.763 3.532 0.363 1.637 0.448 1.552
17 0.203 0.739 3.588 0.378 1.622 0.466 1.534
18 0.194 0.718 3.640 0.391 1.608 0.482 1.518
19 0.187 0.698 3.689 0.403 1.597 0.497 1.503
20 0.180 0.680 3.735 0.415 1.585 0.510 1.490
21 0.173 0.663 3.778 0.425 1.575 0.523 1.477
22 0.167 0.647 3.819 0.434 1.566 0.534 1.466
23 0.162 0.633 3.858 0.443 1.557 0.545 1.455
24 0.157 0.619 3.895 0.451 1.548 0.555 1.445
25 0.153 0.606 3.931 0.459 1.541 0.565 1.435
Control chart constants for X-bar, R, S, Individuals (called "X" or "I" charts), and MR (Moving
Range) Charts.
Notes To construct the "X" and "MR" charts (these are companions) we compute the Moving
Ranges as:
R = range of 1st and 2nd observations, R = range of 2nd and 3rd observations, R = range
2 3 4
of 3rd and 4th observations, etc. with the "average" moving range or "MR-bar" being the
average of these ranges with the "sample size" for each of these ranges being n = 2 since
each is based on consecutive observations ... this should provide an estimated standard
deviation (needed for the "I" chart) of
σ = (MR-bar)/d where the value of d is based on, as just stated, m = 2.
2 2
Similarly, the UCL and LCL for the MR chart will be:
UCL = D (MR-bar) and LCL = D (MR-bar) but, since D = 0 when n = 0 (or, more accurately, is
4 3 3
"not applicable") there will be no LCL for the MR chart, just a UCL.
14.7 Summary
SPC aims at controlling the variability of porocess output using a device called the control
chart.
On a control chart, a certain characteristic of the product is plotted. Under normal conditions
these plotted points are expected to vary in a “usual way” on the chart.
When abnormal points or patterns appear on the chart, it is a statistical indication that the
process parameters or production conditions might have changed undesirably. At this
234 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY