Page 193 - DMGT549_INTERNATIONAL_FINANCIAL_MANAGEMENT
P. 193
International Financial Management
Notes
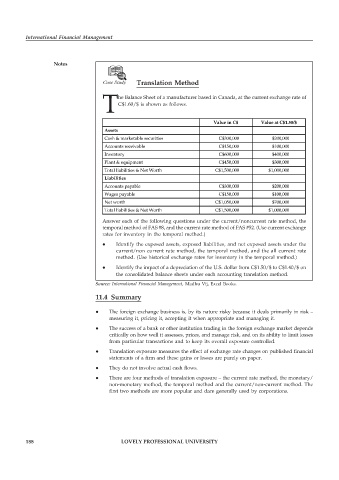
Case Study Translation Method
T he Balance Sheet of a manufacturer based in Canada, at the current exchange rate of
C$1.60/$ is shown as follows.
Value in C$ Value at C$1.50/$
Assets
Cash & marketable securities C$300,000 $200,000
Accounts receivable C$150,000 $100,000
Inventory C$600,000 $400,000
Plant & equipment C$450,000 $300,000
Total liabilities & Net Worth C$1,500,000 $1,000,000
Liabilities
Accounts payable C$300,000 $200,000
Wages payable C$150,000 $100,000
Net worth C$1,050,000 $700,000
Total liabilities & Net Worth C$1,500,000 $1,000,000
Answer each of the following questions under the current/noncurrent rate method, the
temporal method of FAS #8, and the current rate method of FAS #52. (Use current exchange
rates for inventory in the temporal method.)
Identify the exposed assets, exposed liabilities, and net exposed assets under the
current/non current rate method, the temporal method, and the all current rate
method. (Use historical exchange rates for inventory in the temporal method.)
Identify the impact of a depreciation of the U.S. dollar from C$1.50/$ to C$1.40/$ on
the consolidated balance sheets under each accounting translation method.
Source: International Financial Management, Madhu Vij, Excel Books.
11.4 Summary
The foreign exchange business is, by its nature risky because it deals primarily in risk –
measuring it, pricing it, accepting it when appropriate and managing it.
The success of a bank or other institution trading in the foreign exchange market depends
critically on how well it assesses, prices, and manage risk, and on its ability to limit losses
from particular transactions and to keep its overall exposure controlled.
Translation exposure measures the effect of exchange rate changes on published financial
statements of a firm and these gains or losses are purely on paper.
They do not involve actual cash flows.
There are four methods of translation exposure – the current rate method, the monetary/
non-monetary method, the temporal method and the current/non-current method. The
first two methods are more popular and dare generally used by corporations.
188 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY