Page 256 - DMGT552_VISUAL_MERCHANDISING
P. 256
Unit 13: Quality and Process in Visual Merchandising
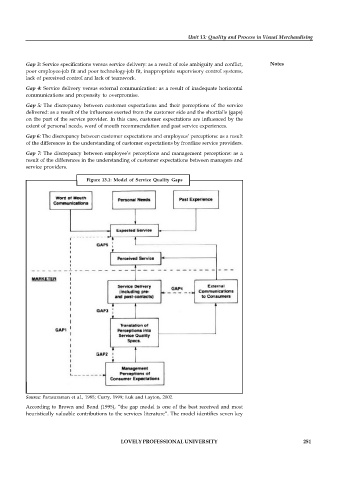
Gap 3: Service specifications versus service delivery: as a result of role ambiguity and conflict, Notes
poor employee-job fit and poor technology-job fit, inappropriate supervisory control systems,
lack of perceived control and lack of teamwork.
Gap 4: Service delivery versus external communication: as a result of inadequate horizontal
communications and propensity to overpromise.
Gap 5: The discrepancy between customer expectations and their perceptions of the service
delivered: as a result of the influences exerted from the customer side and the shortfalls (gaps)
on the part of the service provider. In this case, customer expectations are influenced by the
extent of personal needs, word of mouth recommendation and past service experiences.
Gap 6: The discrepancy between customer expectations and employees’ perceptions: as a result
of the differences in the understanding of customer expectations by frontline service providers.
Gap 7: The discrepancy between employee’s perceptions and management perceptions: as a
result of the differences in the understanding of customer expectations between managers and
service providers.
Figure 13.1: Model of Service Quality Gaps
Source: Parasuraman et al., 1985; Curry, 1999; Luk and Layton, 2002.
According to Brown and Bond (1995), “the gap model is one of the best received and most
heuristically valuable contributions to the services literature”. The model identifies seven key
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 251