Page 174 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 174
Statistical Methods in Economics
Notes The value of this coefficient also ranges between + 1 and – 1. When R is + 1 there is complete agreement
in the order of the rank and the ranks are in the same direction. When R is – 1 there is complete
agreement in the order of the ranks and they are in opposite directions.
In rank correlation we may have two types of problems:
A. Where actual ranks are given.
B. Where ranks are not given.
A. Where Actual Ranks are Given
Where actual ranks are given to us the steps required for computing rank correlation are:
(i) Take the differences of the two ranks, i.e., (R – R ) and denote these differences by D.
1 2
(ii) Square these differences and obtain the total ∑D 2 .
(iii) Apply the formula:
∑
6D 2
R = −1
N 3 − N
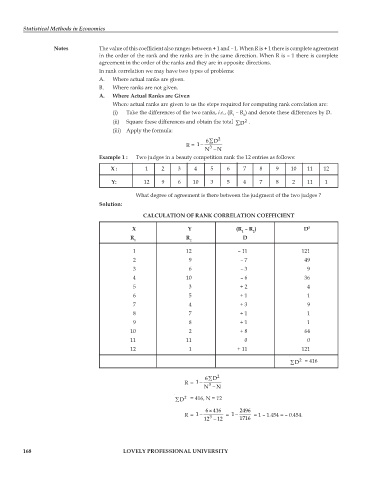
Example 1 : Two judges in a beauty competition rank the 12 entries as follows:
X : 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Y: 12 9 6 10 3 5 4 7 8 2 11 1
What degree of agreement is there between the judgment of the two judges ?
Solution:
CALCULATION OF RANK CORRELATION COEFFICIENT
X Y (R – R ) D 2
1 2
R R D
1 2
1 12 – 11 121
2 9 – 7 49
3 6 – 3 9
4 10 – 6 36
5 3 + 2 4
6 5 + 1 1
7 4 + 3 9
8 7 + 1 1
9 8 + 1 1
10 2 + 8 64
11 11 0 0
12 1 + 11 121
∑D 2 = 416
∑
6D 2
R= −1
N 3 − N
∑D 2 = 416, N = 12
×
6416 2496
R= −1 = −1 = 1 – 1.454 = – 0.454.
12 3 − 12 1716
168 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY