Page 202 - DMTH401_REAL ANALYSIS
P. 202
Real Analysis
Notes
æ 1 ö æ 1 ö 1
f ( )- f ( ) = f ç ÷ - ç f ÷ = 1 0 ³ = e
-
x
x
n N
2 ø
2 ø
è N è N 2
n
æ 0, x Î [1/ , 1]ö
x
Example: Let =I [0,1] and f n ( ) = ç 2 ÷ . Then f does not converge to
x
n
-
è n n x x Î [0,1/ ]ø
any f pointwise nor uniformly.
.
Proof: Look at x = 0. Here f n (0) ¥ Therefore, f does not converge pointwise to any f.
n
Contrapositive tells us that f does not converge uniformly to any f.
n
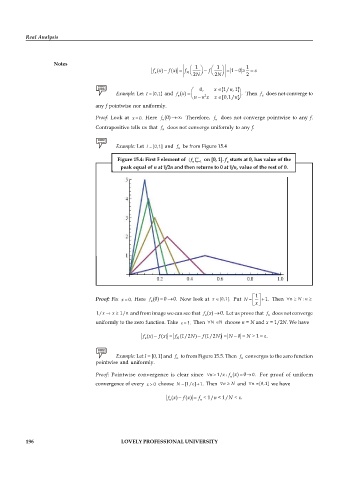
Example: Let =I [0,1] and f be from Figure 15.4
n
¥
Figure 15.4: First 5 element of { f } on [0, 1]. f starts at 0, has value of the
n n = 1 n
peak equal of n at 1/2n and then returns to 0 at 1/n, value of the rest of 0.
é 1 ù
=
Proof: Fix x = 0. Here f n (0) 0 0. Now look at x Î (0,1]. Put N = ê ú + 1. Then " ³n N : n ³
x
ë û
x
x
1/ Þ x ³ 1/n and from image we can see that f n ( ) 0. Let us prove that f does not converge
n
uniformly to the zero function. Take e = 1. Then "N Î choose n = N and x = 1/2N. We have
f ( ) - f ( ) = f (1/2 )- f (1/2 ) = N - 0 = N ³ 1 = e .
x
N
x
N
n N
Example: Let I = [0, 1] and f to from Figure 15.5. Then f converges to the zero function
n n
pointwise and uniformly.
=
x
f
Proof: Pointwise convergence is clear since " >n 1/ : ( ) 0 0. For proof of uniform
x
n
n
+
e
convergence of every e > choose N = [1/ ] 1. Then " ³n N and " Î [0,1] we have
0
x
n
x
f n ( )- f ( ) = f n £ 1/ £ 1/N £ . e
196 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY