Page 160 - DMTH505_MEASURE_THEOREY_AND_FUNCTIONAL_ANALYSIS
P. 160
Unit 12: General Convergence Theorems
Notes
1
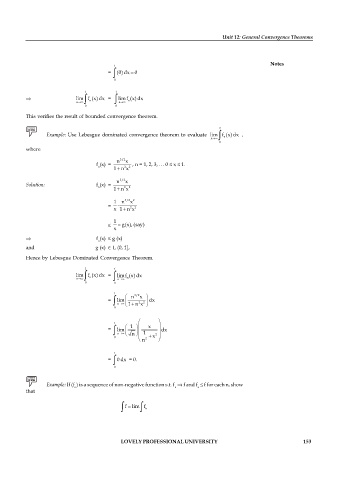
= (0) dx 0
0
1 1
lim f (x) dx = limf (x) dx
n n n n
0 0
This verifies the result of bounded convergence theorem.
1
Example: Use Lebesgue dominated convergence theorem to evaluate lim f (x) dx ,
n n
0
where
n 3/2 x
f (x) = , n = 1, 2, 3, … 0 x 1.
n 2 2
1 n x
n 3/2 x
Solution: f (x) =
n 2 2
1 n x
1 n 3/2 x 2
=
2
x 1 n x 2
1
g(x), (say)
x
f (x) g (x)
n
and g (x) L (0, 1],
Hence by Lebesgue Dominated Convergence Theorem.
1 1
lim f (x) dx = limf (x) dx
n n n n
0 0
1
n 3/2 x
= lim dx
2
n 1 n x 2
0
1
1 x
= lim dx
n n 1 2
0 2 x
n
1
= 0 dx = 0.
0
Example: If (f ) is a sequence of non-negative function s.t. f f and f f for each n, show
n n n
that
f lim f n
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 153