Page 206 - DCOM202_COST_ACCOUNTING_I
P. 206
Cost Accounting – I
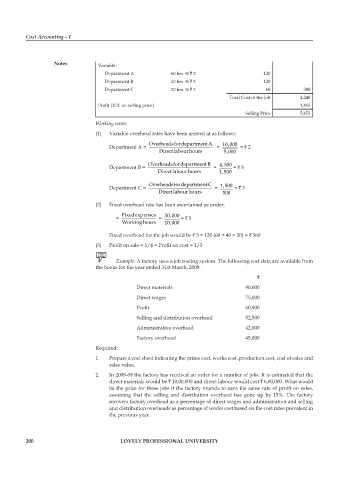
Notes Variable :
Department A 60 hrs. @ ` 2 120
Department B 40 hrs. @ ` 3 120
Department C 20 hrs. @ ` 3 60 300
Total Cost of the Job 4,240
Profit (25% on selling price) 1,413
Selling price 5,653
Working notes:
(1) Variable overhead rates have been arrived at as follows:
OverheadsfordepartmentA 10 000
,
Department A = = = ` 2
Directlabourhours 5 000
,
OverheadsfordepartmentB 4 500
,
Department B = = = ` 3
Directlabourhours 1 500
,
OverheadsfordepartmentC
,
Department C = = 1 500 = ` 3
Directlabourhours 500
(2) Fixed overhead rate has been ascertained as under:
Fixedexp enses 30 000
,
= = = ` 3
Workinghours 10 000
,
Fixed overhead for the job would be ` 3 × 120 (60 + 40 + 20) = ` 360
(3) Profit on sale = 1/4 = Profit on cost = 1/3
Example: A factory uses a job costing system. The following cost data are available from
the books for the year ended 31st March, 2008:
`
Direct materials 90,000
Direct wages 75,000
Profit 60,900
Selling and distribution overhead 52,500
Administrative overhead 42,000
Factory overhead 45,000
Required:
1. Prepare a cost sheet indicating the prime cost, works cost, production cost, cost of sales and
sales value.
2. In 2008-09 the factory has received an order for a number of jobs. It is estimated that the
direct materials would be ` 10,00,000 and direct labour would cost ` 6,00,000. What would
be the price for these jobs if the factory intends to earn the same rate of profit on sales,
assuming that the selling and distribution overhead has gone up by 15%. The factory
recovers factory overhead as a percentage of direct wages and administration and selling
and distribution overheads as percentage of works cost based on the cost rates prevalent in
the previous year.
200 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY