Page 281 - DCOM504_SECURITY_ANALYSIS_AND_PORTFOLIO_MANAGEMENT
P. 281
Security Analysis and Portfolio Management
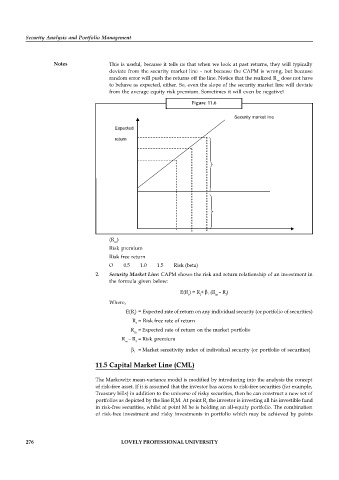
Notes This is useful, because it tells us that when we look at past returns, they will typically
deviate from the security market line – not because the CAPM is wrong, but because
random error will push the returns off the line. Notice that the realized R does not have
m
to behave as expected, either. So, even the slope of the security market line will deviate
from the average equity risk premium. Sometimes it will even be negative!
Figure 11.6
Security market line
Expected
return
(R )
m
Risk premium
Risk free return
O 0.5 1.0 1.5 Risk (beta)
2. Security Market Line: CAPM shows the risk and return relationship of an investment in
the formula given below:
E(R ) = R + i (R – R )
i f m f
Where,
E(R) = Expected rate of return on any individual security (or portfolio of securities)
i
R = Risk free rate of return
f
R = Expected rate of return on the market portfolio
m
R – R = Risk premium
m f
i = Market sensitivity index of individual security (or portfolio of securities)
11.5 Capital Market Line (CML)
The Markowitz mean-variance model is modified by introducing into the analysis the concept
of risk-free asset. If it is assumed that the investor has access to risk-free securities (for example,
Treasury bills) in addition to the universe of risky securities, then he can construct a new set of
portfolios as depicted by the line R M. At point R the investor is investing all his investible fund
f f
in risk-free securities, whilst at point M he is holding an all-equity portfolio. The combination
of risk-free investment and risky investments in portfolio which may be achieved by points
276 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY