Page 283 - DCOM504_SECURITY_ANALYSIS_AND_PORTFOLIO_MANAGEMENT
P. 283
Security Analysis and Portfolio Management
Notes Characteristic Line
A rational investor would not invest in an asset, which does not improve the risk-return
characteristics of his existing portfolio. Since a rational investor would hold the market portfolio,
the asset in question will be added to the market portfolio. MPT derives the required return for
a correctly priced asset in this context.
Specific risk is the risk associated with individual assets - within a portfolio these risks can be
reduced through diversification (specific risks ‘cancel out’). Systematic risk, or market risk,
refers to the risk common to all securities – except for selling short as noted below, systematic
risk cannot be diversified away (within one market). Within the market portfolio, asset-specific
risk will be diversified away to the extent possible. Systematic risk is, therefore, equated with
the risk (standard deviation) of the market portfolio.
Since a security will be purchased only if it improves the risk/return characteristics of the
market portfolio, the risk of a security will be the risk it adds to the market portfolio. In this
context, the volatility of the asset, and its correlation with the market portfolio, is historically
observed and is, therefore, a given (there are several approaches to asset pricing that attempt to
price assets by modelling the stochastic properties of the moments of assets’ returns – these are
broadly referred to as conditional asset pricing models). The (maximum) price paid for any
particular asset (and hence the return it will generate) should also be determined based on its
relationship with the market portfolio.
Systematic risks within one market can be managed through a strategy of using both long and
short positions within one portfolio, creating a ‘market neutral’ portfolio.
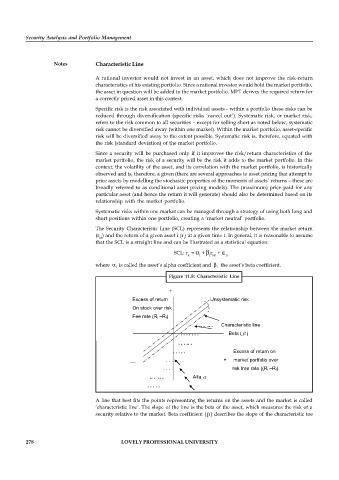
The Security Characteristic Line (SCL) represents the relationship between the market return
(r ) and the return of a given asset i (r ) at a given time t. In general, it is reasonable to assume
M i
that the SCL is a straight line and can be illustrated as a statistical equation:
SCL: r = + r +
it i i Mt it
where is called the asset’s alpha coefficient and i the asset’s beta coefficient.
i
Figure 11.8: Characteristic Line
+
Excess of return Unsystematic risk
On stock over risk
Fee rate (R i –R f)
.. . .. . Characteristic line
. . . . . . . Beta ( )
. . . .. .
. . . . . Excess of return on
__ . . . . . . . + market portfolio over
. . . . risk free rate ((R i –R f)
.. . .. . Alfa
. . . . .
A line that best fits the points representing the returns on the assets and the market is called
CHARACTERISTIC UNI
‘characteristic line’. The slope of the line is the beta of the asset, which measures the risk of a
security relative to the market. Beta coefficient ( ) describes the slope of the characteristic toe
278 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY