Page 98 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 98
Unit 6: Implementation of Combinational Logic Circuit
Notes
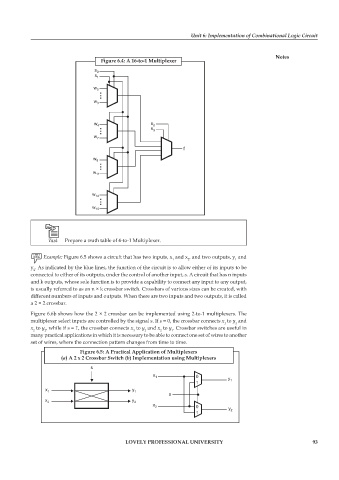
Figure 6.4: A 16-to-1 Multiplexer
Prepare a truth table of 4-to-1 Multiplexer.
Example: Figure 6.5 shows a circuit that has two inputs, x and x , and two outputs, y and
1
1
2
y . As indicated by the blue lines, the function of the circuit is to allow either of its inputs to be
2
connected to either of its outputs, under the control of another input, s. A circuit that has n inputs
and k outputs, whose sole function is to provide a capability to connect any input to any output,
is usually referred to as an n × k crossbar switch. Crossbars of various sizes can be created, with
different numbers of inputs and outputs. When there are two inputs and two outputs, it is called
a 2 × 2 crossbar.
Figure 6.6b shows how the 2 × 2 crossbar can be implemented using 2-to-1 multiplexers. The
multiplexer select inputs are controlled by the signal s. If s = 0, the crossbar connects x to y and
1
1
x to y , while if s = 1, the crossbar connects x to y and x to y . Crossbar switches are useful in
2
1
2
2
1
2
many practical applications in which it is necessary to be able to connect one set of wires to another
set of wires, where the connection pattern changes from time to time.
Figure 6.5: A Practical Application of Multiplexers
(a) A 2 x 2 Crossbar Switch (b) Implementation using Multiplexers
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 93