Page 101 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 101
Digital Circuits and Logic Design
Notes
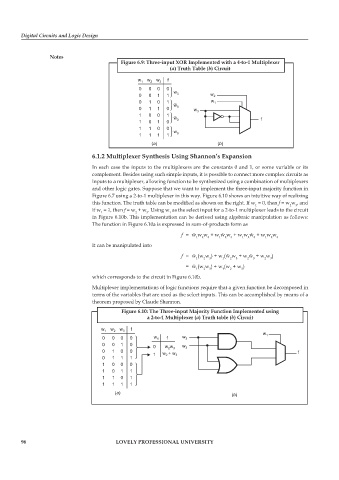
Figure 6.9: Three-input XOR Implemented with a 4-to-1 Multiplexer
(a) Truth Table (b) Circuit
w 1 w 2 w 3 f
0 0 0 0
w
0 0 1 1 3 w 2
0 1 0 1 w 1
w
0 1 1 0 3 w 3
1 0 0 1
w f
1 0 1 0 3
1 1 0 0
w 3
1 1 1 1
a
() ()
b
6.1.2 Multiplexer Synthesis Using Shannon’s Expansion
In each case the inputs to the multiplexers are the constants 0 and 1, or some variable or its
complement. Besides using such simple inputs, it is possible to connect more complex circuits as
inputs to a multiplexer, allowing function to be synthesized using a combination of multiplexers
and other logic gates. Suppose that we want to implement the three-input majority function in
Figure 6.7 using a 2-to-1 multiplexer in this way. Figure 6.10 shows an intuitive way of realizing
this function. The truth table can be modified as shown on the right. If w = 0, then f = w w , and
1
3
2
if w = 1, then f = w + w . Using w as the select input for a 2-to-1 multiplexer leads to the circuit
2
1
3
1
in Figure 6.10b. This implementation can be derived using algebraic manipulation as follows:
The function in Figure 6.10a is expressed in sum-of-products form as
f = ŵ w w + w ŵ w + w w ŵ + w w w 3
3
3
2
1
2
3
1
2
1
1
2
It can be manipulated into
f = ŵ (w w ) + w (ŵ w + w ŵ + w w )
2
1
3
2
3
3
3
1
2
2
= ŵ (w w ) + w (w + w )
1 2 3 1 2 3
which corresponds to the circuit in Figure 6.10b.
Multiplexer implementations of logic functions require that a given function be decomposed in
terms of the variables that are used as the select inputs. This can be accomplished by means of a
theorem proposed by Claude Shannon.
Figure 6.10: The Three-input Majority Function Implemented using
a 2-to-1 Multiplexer (a) Truth table (b) Circuit
w 1 w 2 w 3 f
w
0 0 0 0 w 1 f w 2 1
0 0 1 0 w
0 ww 3 3
2
0 1 0 0 f
1 w + w 3
2
0 1 1 1
1 0 0 0
1 0 1 1
1 1 0 1
1 1 1 1
a
()
()
b
96 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY