Page 89 - DCAP210_INTRODUCTION__TO_MICROPROCESSORS
P. 89
Unit 6: The 8085 Microprocessor Architecture
Notes
Give the basic pin description of the microprocessor architecture.
6.2 Internal Architecture of 8085
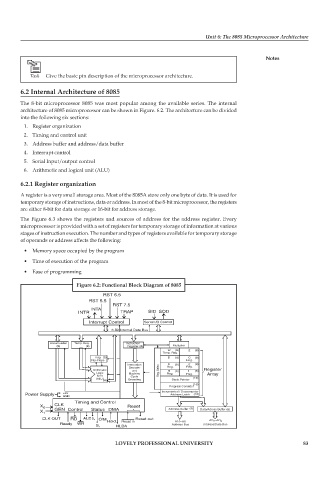
The 8-bit microprocessor 8085 was most popular among the available series. The internal
architecture of 8085 microprocessor can be shown in Figure. 6.2. The architecture can be divided
into the following six sections:
1. Register organization
2. Timing and control unit
3. Address buffer and address/data buffer
4. Interrupt control
5. Serial Input/output control
6. Arithmetic and logical unit (ALU)
6.2.1 Register organization
A register is a very small storage area. Most of the 8085A store only one byte of data. It is used for
temporary storage of instructions, data or address. In most of the 8-bit microprocessor, the registers
are either 8-bit for data storage or 16-bit for address storage.
The Figure 6.3 shows the registers and sources of address for the address register. Every
microprocessor is provided with a set of registers for temporary storage of information at various
stages of instruction execution. The number and types of registers available for temporary storage
of operands or address affects the following:
• Memory space occupied by the program
• Time of execution of the program
• Ease of programming
Figure 6.2: Functional Block Diagram of 8085
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 83