Page 206 - DCAP307_PLANNING_AND_MANAGING_IT_INFRASTRUCTURE
P. 206
Planning and Managing IT Infrastructure
Notes deliver the insight needed to improve overall business performance? From a theoretical
viewpoint, it can. From a practical standpoint, it hasn’t (Table 12.1).
Like decision support, BPM is more than a technology. It involves the processes, methodologies,
metrics and technology used to monitor, measure sand manage a business. Once selected the
business process that has to be improved, and the business methodology to be implemented,
there are the metrics (to monitor, measure and change) to be established. These metrics (key
performance indicators) are defined and selected by the business and not by the IT. The final step
is to choose the business performance measurement technology. We can say that business
intelligence it is just business measurement and not business performance management.
BPM is not a single technology, but rather a combination of elements – BI, scorecarding, profiling.
BI looks at and analyses the past and what has happened up until today – this is useful, as
planning requires knowledge and you can set planning goals based on the past. Scorecarding
enables you measure how you are performing against those planned goals. Every organisation
has processes in place that feed back to the overall plan. What’s new with BPM is the integration
of these processes, methodologies, metrics and systems – an enterprise wide strategy that seeks
to prevent organisations from optimising local business at the expense of overall corporate
performance.
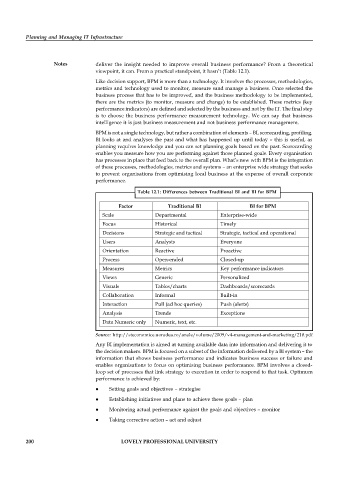
Table 12.1: Differences between Traditional BI and BI for BPM
Factor Traditional BI BI for BPM
Scale Departmental Enterprise-wide
Focus Historical Timely
Decisions Strategic and tactical Strategic, tactical and operational
Users Analysts Everyone
Orientation Reactive Proactive
Process Open-ended Closed-up
Measures Metrics Key performance indicators
Views Generic Personalized
Visuals Tables/charts Dashboards/scorecards
Collaboration Informal Built-in
Interaction Pull (ad hoc queries) Push (alerts)
Analysis Trends Exceptions
Data Numeric only Numeric, text, etc.
Source: http://steconomice.uoradea.ro/anale/volume/2009/v4-management-and-marketing/210.pdf
Any BI implementation is aimed at turning available data into information and delivering it to
the decision makers. BPM is focused on a subset of the information delivered by a BI system – the
information that shows business performance and indicates business success or failure and
enables organisations to focus on optimising business performance. BPM involves a closed-
loop set of processes that link strategy to execution in order to respond to that task. Optimum
performance is achieved by:
Setting goals and objectives – strategise
Establishing initiatives and plans to achieve these goals – plan
Monitoring actual performance against the goals and objectives – monitor
Taking corrective action – act and adjust
200 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY