Page 159 - DCAP601_SIMULATION_AND_MODELING
P. 159
Unit 9: Simulation of a PERT Network (I)
This project model was the first of its kind, a renewal for scientific management, founded by Notes
Frederick Taylor (Taylorism) and later refined by Henry Ford (Fordism). DuPont corporation’s
critical path method was invented at approximately the same time as PERT.
9.3.1 Principle
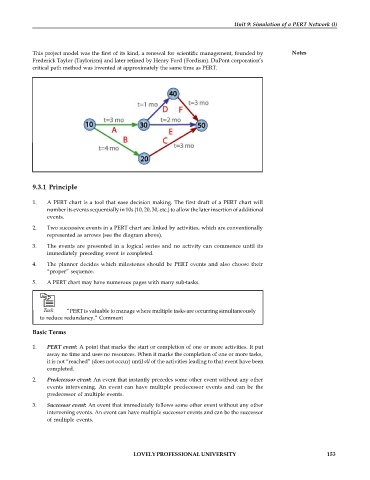
1. A PERT chart is a tool that ease decision making. The first draft of a PERT chart will
number its events sequentially in 10s (10, 20, 30, etc.) to allow the later insertion of additional
events.
2. Two successive events in a PERT chart are linked by activities, which are conventionally
represented as arrows (see the diagram above).
3. The events are presented in a logical series and no activity can commence until its
immediately preceding event is completed.
4. The planner decides which milestones should be PERT events and also choose their
“proper” sequence.
5. A PERT chart may have numerous pages with many sub-tasks.
Task “PERT is valuable to manage where multiple tasks are occurring simultaneously
to reduce redundancy.” Comment
Basic Terms
1. PERT event: A point that marks the start or completion of one or more activities. It put
away no time and uses no resources. When it marks the completion of one or more tasks,
it is not “reached” (does not occur) until all of the activities leading to that event have been
completed.
2. Predecessor event: An event that instantly precedes some other event without any other
events intervening. An event can have multiple predecessor events and can be the
predecessor of multiple events.
3. Successor event: An event that immediately follows some other event without any other
intervening events. An event can have multiple successor events and can be the successor
of multiple events.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 153