Page 161 - DCAP601_SIMULATION_AND_MODELING
P. 161
Unit 9: Simulation of a PERT Network (I)
Notes
Example: When building a house, the land must be graded before the foundation can be
laid)
Example: In the following example there are seven tasks, labeled A through G. Some tasks
can be done concurrently (A and B) while others cannot be done until their predecessor task is
complete (C cannot begin until A is complete). Additionally, each task has three time estimates:
the optimistic time estimate (O), the most likely or normal time estimate (M), and the pessimistic
time estimate (P). The expected time (T ) is computed using the formula (O + 4M + P) ÷ 6.
E
Activity Predecessor Time estimates Expected time
Opt. (O) Normal (M) Pess. (P)
A — 2 4 6 4.00
B — 3 5 9 5.33
C A 4 5 7 5.17
D A 4 6 10 6.33
E B, C 4 5 7 5.17
F D 3 4 8 4.50
G E 3 5 8 5.17
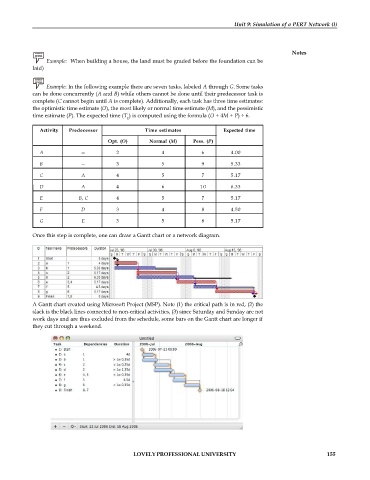
Once this step is complete, one can draw a Gantt chart or a network diagram.
A Gantt chart created using Microsoft Project (MSP). Note (1) the critical path is in red, (2) the
slack is the black lines connected to non-critical activities, (3) since Saturday and Sunday are not
work days and are thus excluded from the schedule, some bars on the Gantt chart are longer if
they cut through a weekend.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 155