Page 158 - DCAP601_SIMULATION_AND_MODELING
P. 158
Simulation and Modelling
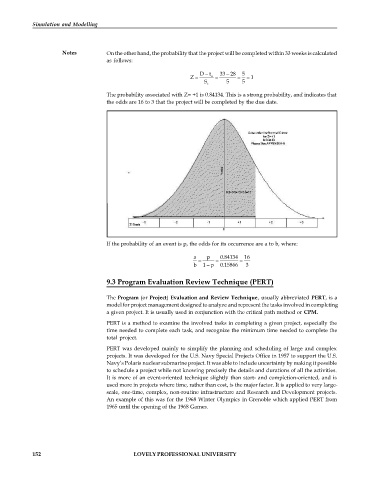
Notes On the other hand, the probability that the project will be completed within 33 weeks is calculated
as follows:
D t 33 28 5
Z e 1
S t 5 5
The probability associated with Z= +1 is 0.84134. This is a strong probability, and indicates that
the odds are 16 to 3 that the project will be completed by the due date.
If the probability of an event is p, the odds for its occurrence are a to b, where:
a p 0.84134 16
b 1 p 0.15866 3
9.3 Program Evaluation Review Technique (PERT)
The Program (or Project) Evaluation and Review Technique, usually abbreviated PERT, is a
model for project management designed to analyze and represent the tasks involved in completing
a given project. It is usually used in conjunction with the critical path method or CPM.
PERT is a method to examine the involved tasks in completing a given project, especially the
time needed to complete each task, and recognize the minimum time needed to complete the
total project.
PERT was developed mainly to simplify the planning and scheduling of large and complex
projects. It was developed for the U.S. Navy Special Projects Office in 1957 to support the U.S.
Navy’s Polaris nuclear submarine project. It was able to include uncertainty by making it possible
to schedule a project while not knowing precisely the details and durations of all the activities.
It is more of an event-oriented technique slightly than start- and completion-oriented, and is
used more in projects where time, rather than cost, is the major factor. It is applied to very large-
scale, one-time, complex, non-routine infrastructure and Research and Development projects.
An example of this was for the 1968 Winter Olympics in Grenoble which applied PERT from
1965 until the opening of the 1968 Games.
152 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY