Page 180 - DMGT501_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 180
Operations Management
Notes Quality Control during Production
The Standard Quality is determined through careful research & investigation. It is quite
impracticle to adhere strictly to the standards of precision, especially in cases where human
factor dominates over the machine factor. Some deviation is therefore, allowed or tolerated.
They are referred to as tolerances. Within the limits, set by these tolerances, the product is
considered to be of standard quality. SQC brings to light the deviations outside these limits, i.e.
the purpose of Statistical Quality Control is to discover and correct only those forces which are
also responsible for variations outside the suitable pattern through SQC techniques.
While acceptance through sampling is used for controlling the materials input to the process,
the process itself may be controlled by Statistical Sampling procedures i.e. by taking samples
from the output of the process. The samples may be checked for:
1. Their measurable characteristics such as length, diameter, hardness, tensile strength etc.
2. ‘Fraction Defectives’ “p”, when the characteristics cannot or need not to be measured.
3. Number of defects in the sample (c).
The Process is said to be within control if the sample points fall within the pre-established
control limits. The crux of the Process Control lies in establishing the appropriate control limits.
The charts showing these control limits are called ‘Process Control Charts’.
Kinds of Process Control Charts
1. Sampling means chart (x);
2. Fraction Defections charts or ‘p’ chart; and
3. Number of Defects chart or ‘c’ chart.
Problems on Control Charts
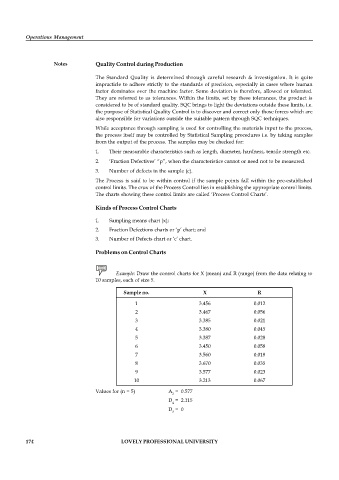
Example: Draw the control charts for X (mean) and R (range) from the data relating to
10 samples, each of size 5.
Sample no. X R
1 3.456 0.012
2 3.467 0.056
3 3.385 0.021
4 3.380 0.045
5 3.387 0.028
6 3.450 0.058
7 3.560 0.018
8 3.670 0.035
9 3.577 0.023
10 3.213 0.067
Values for (n = 5) A = 0.577
2
D = 2.115
4
D = 0
3
174 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY