Page 142 - DMGT550_RETAIL_MANAGEMENT
P. 142
Unit 8: Human Resource Management in Retail
Herzberg’s two Factor Theory of Motivation Notes
This theory classifies the two factors of motivation as, hygiene factors which are basically the
physiological and safety needs of Maslow’s model. The motivators here are the esteem needs
and self actualisation. According to the fury lies in tatters are extrinsic to the individual and
motivators are intrinsic to the individual.
McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y
Theory X simply lays down that employees if not supervised and not motivated with negative
motivation would not like to contribute to the cause of the organisation at all. On the other
hand, theory Y views employees as self motivated and enjoy work but would also like to
contribute to the organisation without any supervision or pressure. Another theory which was
propounded on the basis of these two theories was theory Z derived from the above theories to
prove that individuals need both positive as well as negative motivation depending upon the
circumstances. Therefore, it can be suggested to the human resource department of a retail store
to motivate their employees depending upon an individual mindset as well as the stage of his
life.
These theories of motivation were propounded based on years of research. However a retail
store can adopt any of them or create a hybrid from these depending, upon the ground realities.
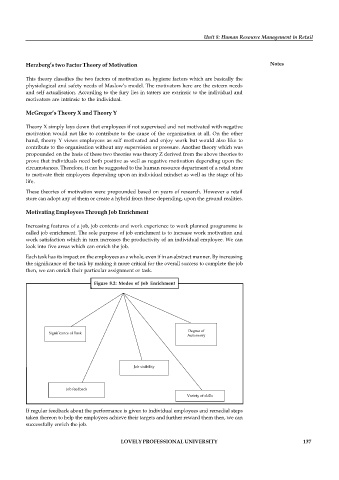
Motivating Employees Through Job Enrichment
Increasing features of a job, job contents and work experience to work planned programme is
called job enrichment. The sole purpose of job enrichment is to increase work motivation and
work satisfaction which in turn increases the productivity of an individual employee. We can
look into five areas which can enrich the job.
Each task has its impact on the employees as a whole, even if in an abstract manner. By increasing
the significance of the task by making it more critical for the overall success to complete the job
then, we can enrich their particular assignment or task.
Figure 8.2: Modes of Job Enrichment
Degree of
Significance of Task
Autonomy
Job visibility
Job feedback
Variety of skills
If regular feedback about the performance is given to individual employees and remedial steps
taken thereon to help the employees achieve their targets and further reward them then, we can
successfully enrich the job.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 137