Page 106 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 106
Statistical Methods in Economics
Notes Solution:
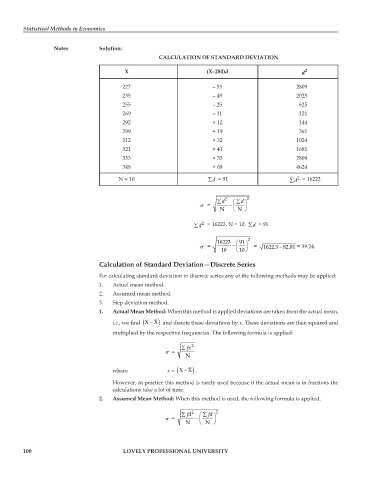
CALCULATION OF STANDARD DEVIATION
X (X–280)d d 2
227 – 53 2809
235 – 45 2025
255 – 25 625
269 – 11 121
292 + 12 144
299 + 19 361
312 + 32 1024
321 + 41 1681
333 + 53 2809
348 + 68 4624
N = 10 ∑d = 91 ∑d = 16223
2
∑ 2 ⎛ ∑d d ⎞ 2
σ = − ⎜ ⎟
⎝ N ⎠ N
∑d 2 = 16223, N = 10, ∑d = 91
16223 ⎛ ⎞ 91 2
−
σ = − ⎜ ⎟ = 1622.3 82.81 = 39.24.
10 ⎝ ⎠ 10
Calculation of Standard Deviation—Discrete Series
For calculating standard deviation in discrete series any of the following methods may be applied:
1. Actual mean method.
2. Assumed mean method.
3. Step deviation method.
1. Actual Mean Method: When this method is applied deviations are taken from the actual mean,
i.e., we find ( XX and denote these deviations by x. These deviations are then squared and
) −
multiplied by the respective frequencies. The following formula is applied:
∑ fx 2
σ =
N
) −
where x = ( XX .
However, in practice this method is rarely used because if the actual mean is in fractions the
calculations take a lot of time.
2. Assumed Mean Method: When this method is used, the following formula is applied.
∑ 2 ⎛ ∑ fd fd ⎞ 2
σ = − ⎜ ⎟
⎝ N ⎠ N
100 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY