Page 109 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 109
Unit 7: Mean Deviation and Standard Deviation
Notes
(iii) Multiply the frequency of each class with these deviations and obtain ∑ fd .
(iv) Square the deviations and multiply them with the respective frequencies of each
2
class and obtain ∑ fd .
Thus, the only difference in procedure in case of continuous series is to find mid-
points of the various classes.
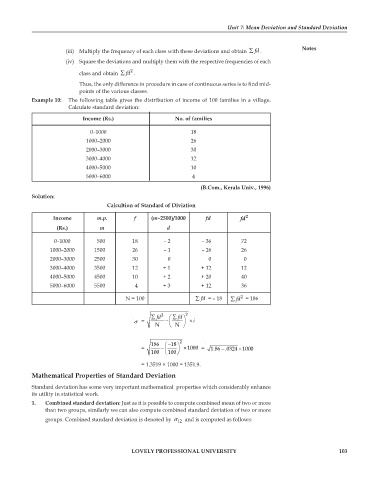
Example 10: The following table gives the distribution of income of 100 families in a village.
Calculate standard deviation:
Income (Rs.) No. of families
0–1000 18
1000–2000 26
2000–3000 30
3000–4000 12
4000–5000 10
5000–6000 4
(B.Com., Kerala Univ., 1996)
Solution:
Calcultion of Standard of Diviation
Income m.p. f (m–2500)/1000 fd fd 2
(Rs.) m d
0–1000 500 18 – 2 – 36 72
1000–2000 1500 26 – 1 – 26 26
2000–3000 2500 30 0 0 0
3000–4000 3500 12 + 1 + 12 12
4000–5000 4500 10 + 2 + 20 40
5000–6000 5500 4 + 3 + 12 36
2
N = 100 ∑ fd = – 18 ∑ fd = 186
∑ 2 ⎛ ∑ fd fd ⎞ 2
σ = − ⎜ ⎟ × i
⎝ N ⎠ N
186 ⎛ − 18 ⎞ 2
−
×
= − ⎜ ⎟ × 1000 = 1.86 .0324 1000
100 ⎝ 100 ⎠
= 1.3519 × 1000 = 1351.9.
Mathematical Properties of Standard Deviation
Standard deviation has some very important mathematical properties which considerably enhance
its utility in statistical work.
1. Combined standard deviation: Just as it is possible to compute combined mean of two or more
than two groups, similarly we can also compute combined standard deviation of two or more
groups. Combined standard deviation is denoted by σ 12 and is computed as follows:
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 103