Page 112 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 112
Statistical Methods in Economics
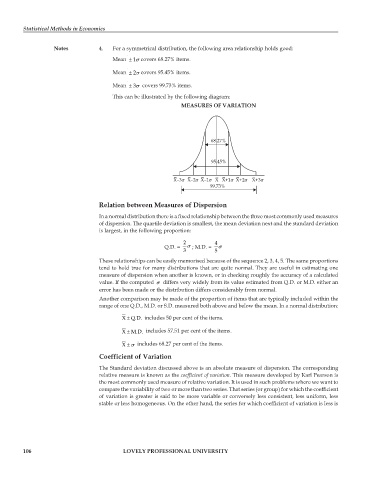
Notes 4. For a symmetrical distribution, the following area relationship holds good:
σ
Mean ± 1 covers 68.27% items.
σ
Mean ± 2 covers 95.45% items.
σ
Mean ± 3 covers 99.73% items.
This can be illustrated by the following diagram:
MEASURES OF VARIATION
68.27%
95.45%
X–3 X–2 X–1 X X+1 X+2 X+3
99.73%
Relation between Measures of Dispersion
In a normal distribution there is a fixed relationship between the three most commonly used measures
of dispersion. The quartile deviation is smallest, the mean deviation next and the standard deviation
is largest, in the following proportion:
2 4
Q.D. = σ ; M.D. = σ
3 5
These relationships can be easily memorised because of the sequence 2, 3, 4, 5. The same proportions
tend to hold true for many distributions that are quite normal. They are useful in estimating one
measure of dispersion when another is known, or in checking roughly the accuracy of a calculated
value. If the computed σ differs very widely from its value estimated from Q.D. or M.D. either an
error has been made or the distribution differs considerably from normal.
Another comparison may be made of the proportion of items that are typically included within the
range of one Q.D., M.D. or S.D. measured both above and below the mean. In a normal distribution:
±
XQ.D. includes 50 per cent of the items.
XM.D. includes 57.51 per cent of the items.
±
X σ includes 68.27 per cent of the items.
±
Coefficient of Variation
The Standard deviation discussed above is an absolute measure of dispersion. The corresponding
relative measure is known as the coefficient of variation. This measure developed by Karl Pearson is
the most commonly used measure of relative variation. It is used in such problems where we want to
compare the variability of two or more than two series. That series (or group) for which the coefficient
of variation is greater is said to be more variable or conversely less consistent, less uniform, less
stable or less homogeneous. On the other hand, the series for which coefficient of variation is less is
106 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY